Cytokine changes in fatal cases of paraquat poisoning
- PMID: 34786083
- PMCID: PMC8581908
Cytokine changes in fatal cases of paraquat poisoning
Abstract
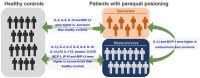
Cytokine-mediated inflammation is involved in the pathophysiology of paraquat toxicity. Nevertheless, few human studies have examined fluctuations in circulating cytokine levels. Blood samples were obtained from 21 patients with paraquat poisoning and compared to those of 18 healthy controls. All paraquat patients received a standard detoxification protocol composed of hemoperfusion, pulse therapies of methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide, followed by dexamethasone therapy. Nonsurvivors not only had higher scores for the severity index of paraquat poisoning (P=0.004) but also presented with higher white blood cell counts (P=0.046) than survivors. Multiplex immunoassays revealed higher circulating levels of interleukin 2 (IL-2), interleukin 9 (IL-9), interleukin 10 (IL-10) and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 beta (MIP-1β) in survivors than in healthy controls. Furthermore, the circulating levels of interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), IL-2, interleukin 5 (IL-5), interleukin 8 (IL-8), IL-9, IL-10, interleukin 12 (IL-12 p70), interleukin 17A (IL-17A), eotaxin, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP-10) and MIP-1β were higher in nonsurvivors than in healthy controls. Finally, the circulating levels of IL-1β and MCP-1 were higher in nonsurvivors than in survivors. Therefore, the observation of cytokine-mediated inflammation is in line with the detoxification protocol because glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide are potent anti-inflammatory agents. Additionally, circulating levels of IL-1β and MCP-1 could serve as promising prognostic markers for patients with paraquat poisoning.
Keywords: Paraquat poisoning; cytokine; inflammation; mortality; multiplex immunoassays; severity index of paraquat poisoning.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cytokine and Chemokine Concentration in the Tear of Patients with Age-Related Cataract.Curr Eye Res. 2020 Sep;45(9):1101-1106. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1715445. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Curr Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 31928443
-
Multiplex determination of murine seminal fluid cytokine profiles.Reproduction. 2006 Mar;131(3):613-21. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.00959. Reproduction. 2006. PMID: 16514204
-
Validation of Sputum Biomarker Immunoassays and Cytokine Expression Profiles in COPD.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 11;10(8):1949. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081949. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009496 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating interleukin (IL)-8, IL-2R, IL-12, and IL-15 levels are independently prognostic in primary myelofibrosis: a comprehensive cytokine profiling study.J Clin Oncol. 2011 Apr 1;29(10):1356-63. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.32.9490. Epub 2011 Feb 7. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21300928
-
Systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive exercise. Cytokine kinetics.Exerc Immunol Rev. 2002;8:6-48. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12690937 Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic and Lung Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Associated With Behavioral Changes Induced by Inhaled Paraquat Are Ameliorated by Carvacrol.PPAR Res. 2024 Aug 24;2024:4049448. doi: 10.1155/2024/4049448. eCollection 2024. PPAR Res. 2024. PMID: 39221092 Free PMC article.
-
Human Poisoning with Chlorpyrifos and Cypermethrin Pesticide Mixture: Assessment of Clinical Outcome of Cases Admitted in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Taiwan.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Oct 26;16:4795-4804. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S432861. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37908758 Free PMC article.
-
Human Poisoning with Methomyl and Cypermethrin Pesticide Mixture.Toxics. 2023 Apr 14;11(4):372. doi: 10.3390/toxics11040372. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37112599 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Metabolic and Gut Microbiome Responses to Paraquat Administration in Male Wistar Rats: Implications for Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 1;13(1):67. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010067. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247491 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Responses to COVID-19 Vaccines in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Lead Exposure.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 30;23(23):15003. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315003. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yen TH, Wang IK, Hsu CW. Hemoperfusion for paraquat poisoning. Kidney Int. 2018;94:1239. - PubMed
-
- Lee HL, Lin HJ, Yeh SY, Chi CH, Guo HR. Etiology and outcome of patients presenting for poisoning to the emergency department in Taiwan: a prospective study. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2008;27:373–379. - PubMed
-
- Suntres ZE. Role of antioxidants in paraquat toxicity. Toxicology. 2002;180:65–77. - PubMed
-
- Yang CJ, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Weng CH, Hsu CW, Lee SY, Lee SH, Chang CM, Lin WR, Yen TH. Spectrum of toxic hepatitis following intentional paraquat ingestion: analysis of 187 cases. Liver Int. 2012;32:1400–1406. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
