The analgesic effect and inflammatory mechanism of nonsteroidal analgesics combined with nerve block in post-gynecologic surgery patients
- PMID: 34786086
- PMCID: PMC8581877
The analgesic effect and inflammatory mechanism of nonsteroidal analgesics combined with nerve block in post-gynecologic surgery patients
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the analgesic effect and inflammatory mechanism of nonsteroidal analgesics combined with nerve block in post-gynecologic surgery patients.
Methods: Sixty patients who underwent gynecological laparotomies in our hospital were enrolled in this retrospective cohort study, with 30 patients administered nonsteroidal analgesics combined with nerve block (the observation group) and 30 patients administered nonsteroidal analgesics alone (the control group). The patients in the observation group were administered an intravenous injection of flurbiprofen axetil 1 mg/kg before the end of the operation, and 0.375% ropivacaine was used for bilateral transversus abdominis plane block after the operation. The patients in the control group were administered only an intravenous injection of flurbiprofen axetil 1 mg/kg before the end of the operation. The blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), visual analogue scale (VAS) scores, and the numerical rating scale (NRS) scores were recorded before the operation (T0) and at 1 h (T1), 6 h (T2), 12 h (T3), and 24 h (T4) after the recovery from the anesthesia. The incidences of emergence agitation, and the operation and recovery times in the two groups were recorded. Blood samples were collected before and at one day after the operations to measure the inflammatory factor levels such as IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α.
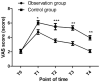
Results: The BP, HR, and the VAS and NRS scores in the observation group at T1, T2, T3, and T4 were lower than they were in the control group (P<0.01). The inflammatory factor levels after the operation in the observation group were lower than they were in the control group (P<0.01). There was no significant difference in the incidences of complications between the two groups (P>0.05).
Conclusion: Flurbiprofen axetil combined with ropivacaine for bilateral transversus abdominis plane block has a significant analgesic effect on patients after gynecologic surgery. The mechanism may be due to the fact that nonsteroidal analgesics combined with nerve block further reduce the inflammatory factors in the body, which proves the superiority of multimodal analgesia.
Keywords: Flurbiprofen axetil; bilateral transversus abdominis plane block; multimodal combined analgesia.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multimodal analgesia with ropivacaine wound infiltration and intravenous flurbiprofen axetil provides enhanced analgesic effects after radical thyroidectomy: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2019 Aug 31;19(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0835-2. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 31470813 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasound Image-Guided Nerve Block Combined with General Anesthesia under an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm on Patients Undergoing Radical Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer during and after Operation.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jan 19;2022:6914157. doi: 10.1155/2022/6914157. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9810538. doi: 10.1155/2023/9810538. PMID: 35096134 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
[Postoperative analgesia with fentanyl combined with flurbiprofen axetil following gynecologic surgery for turnor].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009 Feb;29(2):313-5. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 19246310 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Comparing post-operative analgesic effects of varying doses of dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to ropivacaine for ultrasound-guided dual transversus abdominis plane block following laparotomy for gynecologic malignancies.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Aug;20(2):860-867. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8787. Epub 2020 May 25. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32765653 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparative study between electroacupuncture at Neima point and Neiguan (PC 6) and epidural nerve block for preemptive analgesia in patients undergoing thoracic surgery].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2021 Jan 12;41(1):59-64. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20200121-k0001. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2021. PMID: 33559444 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
References
-
- Hou PC, Lin FJ, Lin SY, Hwang TJ, Wang CC. Risk of intracranial hemorrhage with concomitant use of antidepressants and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a nested case-control study. Ann Pharmacother. 2021;55:941–948. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Wu H, Wang R. Effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on Barrett’s esophagus risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2021;45:101552. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
