Fine nursing intervention relieves the clinical symptoms and decreases the adverse events in acute alcoholism patients
- PMID: 34786093
- PMCID: PMC8581946
Fine nursing intervention relieves the clinical symptoms and decreases the adverse events in acute alcoholism patients
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study is to explore the effect of fine nursing interventions on the clinical efficacy of acute alcoholism patients (AA).
Methods: A total of 100 patients with AA were included in the study. Among them, 51 patients who underwent fine nursing intervention were assigned to the research group (RG), and the remaining 49 patients were treated with routine nursing intervention and were assigned to the control group (CG). The nursing efficacy, the recovery times (consciousness and limb movement), the incidences of adverse events, the nursing compliance, the psychological states (the Symptom Checklist 90 and SCL-90 scores), and the nursing satisfaction levels were observed and compared between the two groups.
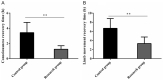
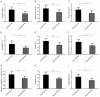
Results: Compared with the CG, the nursing efficacy, the compliance, and the nursing satisfaction levels in the RG were markedly higher, while the consciousness and limb movement recovery times were significantly shorter; moreover, the RG presented a significantly lower incidence of adverse events and SCL-90 scores than the CG.
Conclusion: While validly relieving the clinical symptoms and reducing the incidence of adverse events, fine nursing can effectively promote the recovery of patients with AA, and improve their treatment compliance and psychological states.
Keywords: Fine nursing; acute alcoholism; adverse events; clinical symptoms; prevention.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of high-quality nursing intervention on psychological emotion, life quality and nursing satisfaction of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy.Am J Transl Res. 2021 May 15;13(5):4928-4938. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34150077 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-based nursing intervention can improve the treatment compliance, quality of life and self-efficacy of patients with lung cancer undergoing radiotherapy and chemotherapy.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Jan 15;14(1):396-405. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35173858 Free PMC article.
-
High-quality nursing intervention can improve negative emotions, quality of life and activity of daily living of elderly patients with Parkinson's disease.Am J Transl Res. 2021 May 15;13(5):4749-4759. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34150055 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of primary nursing intervention for elderly patients with cancer pain on the improvement of potential risk and pain degree.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Oct 15;13(10):11890-11898. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34786119 Free PMC article.
-
The risk factors of autogenous arteriovenous fistula dysfunction in maintenance hemodialysis patients and the curative effect of personalized nursing.Am J Transl Res. 2021 May 15;13(5):5107-5116. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34150099 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Study on the Application of the Concept of Childlike Interest with Refined Nursing Intervention in the Treatment of Children with Severe Pneumonia.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Aug 3;2022:5360733. doi: 10.1155/2022/5360733. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9891735. doi: 10.1155/2023/9891735. PMID: 35966238 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Weizmannia coagulans BC99 Enhances Intestinal Barrier Function by Modulating Butyrate Formation to Alleviate Acute Alcohol Intoxication in Rats.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 29;16(23):4142. doi: 10.3390/nu16234142. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39683538 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Refined Nursing Combined with Comprehensive Treatment of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in Gastrointestinal Dysfunction after Tumor Operation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 20;2022:4957061. doi: 10.1155/2022/4957061. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35911141 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating network pharmacology and experimental verification to explore the mechanism of puerarin against oliguria in acute alcoholism.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 10;13:1006660. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1006660. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36299877 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Human-Oriented Fine Nursing on Psychological Emotion, Life Quality, and Nursing Satisfaction of Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 8;2022:5016967. doi: 10.1155/2022/5016967. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9859058. doi: 10.1155/2023/9859058. PMID: 35979011 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Studer J, Gmel G, Bertholet N, Marmet S, Daeppen JB. Alcohol-induced blackouts at age 20 predict the incidence, maintenance and severity of alcohol dependence at age 25: a prospective study in a sample of young Swiss men. Addiction. 2019;114:1556–1566. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Y, Lu H, Han J, Jiang H, Li S, Chen X, Lin P. Using of pre-hospital emergency resources by acute alcoholism patients in a hospital in Guangzhou: a data survey from 2009 to 2018. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019;31:1411–1415. - PubMed
-
- Du A, Dai X, Dong J, Liu J, Zhang Y, Fu P, Qin H, Li R, Zhang R. Effects of aminooxyacetic acid on hippocampal mitochondria in rats with chronic alcoholism: the analysis of learning and memory-related genes. J Integr Neurosci. 2019;18:451–462. - PubMed
-
- Erokhin IuA, Paukov VS, Kirillov IuA. Causes of the people death from drunkenness and alcoholism. Arkh Patol. 2012;74:33–36. - PubMed
-
- Xu JF, Lu JJ, Cao Y, Wang W, Li HH, Chen JG, Wang F, Wu PF. Sulforaphane alleviates ethanol-mediated central inhibition and reverses chronic stress-induced aggravation of acute alcoholism via targeting Nrf2-regulated catalase expression. Neuropharmacology. 2020;176:108235. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
