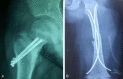
Treatment effect of elastic intramedullary nail reduction and fixation on children with femoral neck fractures
- PMID: 34786145
- PMCID: PMC8581856
Treatment effect of elastic intramedullary nail reduction and fixation on children with femoral neck fractures
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the treatment effect of elastic intramedullary nail reduction and fixation on children with femoral neck fractures.
Methods: Sixty-two children with femoral neck fractures in our hospital were equally divided into the open reduction and Kirschner wire internal fixation group (group O) and elastic intramedullary nail reduction and fixation group (group E). We investigated the differences in fracture healing time, intraoperative situation, clinical efficacy, Harris scores, secondary effects and bone healing time between group O and group E.
Results: The intraoperative indexes such as operation time and blood loss of group E were significantly lower than those of group O (P<0.05). After the operation, the treatment effect of group E was slightly higher than that of group O, but there was no significant difference (P>0.05). The Harris score of group E was significantly higher than that of group O (P<0.05). The fracture healing time and bone healing time after the surgery in group E were significantly shorter than those in group O (P<0.05). The incidence of secondary effects in group E was lower than that in group O, but without significant difference (P>0.05).
Conclusion: Elastic intramedullary nail reduction and fixation has a better effect in the treatment of children with femoral neck fractures, which can accelerate fracture healing time and improve children's hip function after the operation.
Keywords: Femoral neck fractures; children; elastic intramedullary nail reduction and fixation; treatment effect.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Kirschner wire retractor-assisted reduction and inverted insertion of elastic nail in the treatment of children's irreducible subradial 1/3 fractures].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022 Aug 25;35(8):752-6. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2022.08.010. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022. PMID: 35979769 Chinese.
-
Intramedullary Nail Fixation Assisted by Orthopaedic Robot Navigation for Intertrochanteric Fractures in Elderly Patients.Orthop Surg. 2019 Apr;11(2):255-262. doi: 10.1111/os.12447. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Orthop Surg. 2019. PMID: 31004410 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures with Cannulated Screw Invasive Internal Fixation Assisted by Orthopaedic Surgery Robot Positioning System.Orthop Surg. 2019 Oct;11(5):864-872. doi: 10.1111/os.12548. Orthop Surg. 2019. PMID: 31663277 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of intramedullary nail fixation following two step closed reduction or limited open reduction for femoral subtrochanteric fractures].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2021 Sep 25;34(9):826-9. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2021.09.007. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2021. PMID: 34569206 Chinese.
-
Treatment of pediatric femoral shaft fractures with elastic stable intramedullary nails versus external fixation: A meta-analysis.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020 Nov;106(7):1305-1311. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2020.06.012. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33082120
References
-
- Shigemura T. Letter to the editor regarding “treatment of non-united femoral neck fracture by a novel subtrochanteric angulation lateral translation valgus osteotomy (SALVA osteotomy)” by Hegazy et al. Int Orthop. 2020;44:2185. - PubMed
-
- Zajonz D, Brand A, Lycke C, Özkurtul O, Theopold J, Spiegl UJA, Roth A, Josten C, Fakler JKM. Risk factors for early infection following hemiarthroplasty in elderly patients with a femoral neck fracture. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2019;45:207–212. - PubMed
-
- Sanz-Reig J, Lizaur-Utrilla A, Serna-Berna R. Outcomes in nonagenarians after hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fracture. A prospective matched cohort study. Hip Int. 2012;22:113–118. - PubMed
-
- Lin ZE, Zheng H, Chen XS, Li ZH. Analysis of curative effect of traditional chinese bone setting manipulation for the treatment of femoral neck fracture. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2018;31:115–119. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources