Non-coding RNA basis of muscle atrophy
- PMID: 34786211
- PMCID: PMC8569427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.10.010
Non-coding RNA basis of muscle atrophy
Abstract
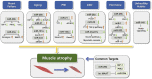
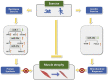
Muscle atrophy is a common complication of many chronic diseases including heart failure, cancer cachexia, aging, etc. Unhealthy habits and usage of hormones such as dexamethasone can also lead to muscle atrophy. However, the underlying mechanisms of muscle atrophy are not completely understood. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), such as microRNAs (miRNAs), long ncRNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), play vital roles in muscle atrophy. This review mainly discusses the regulation of ncRNAs in muscle atrophy induced by various factors such as heart failure, cancer cachexia, aging, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), peripheral nerve injury (PNI), chronic kidney disease (CKD), unhealthy habits, and usage of hormones; highlights the findings of ncRNAs as common regulators in multiple types of muscle atrophy; and summarizes current therapies and underlying mechanisms for muscle atrophy. This review will deepen the understanding of skeletal muscle biology and provide new strategies and insights into gene therapy for muscle atrophy.
Keywords: aging; heart failure; lncRNA; microRNA; muscle atrophy; non-coding RNA.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Regulating Cachexia Muscle Atrophy.Cells. 2024 Sep 27;13(19):1620. doi: 10.3390/cells13191620. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39404384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Atrophy in Cachexia by MicroRNAs and Long Non-coding RNAs.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 15;8:577010. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.577010. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33043011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Analysis of Differentially Expressed Coding and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Multiple Models of Skeletal Muscle Atrophy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 4;22(5):2558. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052558. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33806354 Free PMC article.
-
A transcriptomic profile of topping responsive non-coding RNAs in tobacco roots (Nicotiana tabacum).BMC Genomics. 2019 Nov 14;20(1):856. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6236-6. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31726968 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs: key players in cardiac disease.J Physiol. 2020 Jul;598(14):2995-3003. doi: 10.1113/JP278131. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31291008 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of non-coding RNAs in muscle aging: regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jan 9;10:1308274. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1308274. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38264571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myogenic microRNAs as Therapeutic Targets for Skeletal Muscle Mass Wasting in Breast Cancer Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 18;25(12):6714. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126714. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a novel small-molecule inhibitor of miR-29b attenuates muscle atrophy.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Feb 4;31:527-540. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.02.003. eCollection 2023 Mar 14. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 36891498 Free PMC article.
-
Human myofiber-enriched aging-induced lncRNA FRAIL1 promotes loss of skeletal muscle function.Aging Cell. 2024 Apr;23(4):e14097. doi: 10.1111/acel.14097. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38297807 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Exercise and Aging on Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Skeletal Muscle: Roles of ROS and Epigenetics.Cells. 2022 Jun 30;11(13):2086. doi: 10.3390/cells11132086. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources