BRASH Syndrome Leading to Cardiac Arrest and Diffuse Anoxic Brain Injury: An Underdiagnosed Entity
- PMID: 34786229
- PMCID: PMC8580112
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.18628
BRASH Syndrome Leading to Cardiac Arrest and Diffuse Anoxic Brain Injury: An Underdiagnosed Entity
Abstract
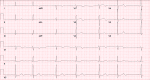
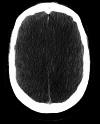
BRASH (bradycardia, renal failure, atrioventricular [AV] nodal blocking medications, shock, hyperkalemia) syndrome describes the phenomenon of profound bradycardia from a combination of hyperkalemia and use of AV nodal blocking medication with underlying renal injury. We present a case of BRASH syndrome in a patient on chronic beta-blocker therapy for his coronary artery disease who presented with life-threatening hyperkalemia and acute renal failure. Due to failure in early recognition and superimposed effect with further beta-blocker dosing, the patient developed profound bradycardia and later went into pulseless electrical activity cardiac arrest requiring cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Metabolic derangements and bradycardia later resolved with medical management, but unfortunately, the patient developed diffuse anoxic brain injury after the cardiac arrest and was declared brain dead.
Keywords: av nodal blocking medications; bradycardia; brash; cardiac arrest; ecg (electrocardiogram); hyperkalemia; renal failure.
Copyright © 2021, Ghumman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Interplay Between Hypocalcemia and Atrioventricular Nodal Blocking Agents in Inducing a Bradycardia, Renal Failure, Atrioventricular Nodal Blockade, Shock, and Hyperkalemia (BRASH)-Like Phenomenon With Serial Serum Drug Concentrations.Cureus. 2025 Feb 12;17(2):e78925. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78925. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40091947 Free PMC article.
-
Two Cases of BRASH Syndrome: A Diagnostic Challenge.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2022 Apr 8;9(4):003314. doi: 10.12890/2022_003314. eCollection 2022. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35520368 Free PMC article.
-
BRASH Syndrome: Bradycardia, Renal Failure, AV Blockade, Shock, and Hyperkalemia.J Emerg Med. 2020 Aug;59(2):216-223. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2020.05.001. Epub 2020 Jun 18. J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32565167
-
Clinical characteristics of BRASH syndrome: Systematic scoping review.Eur J Intern Med. 2022 Sep;103:57-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2022.06.002. Epub 2022 Jun 5. Eur J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35676108
-
From Salvador Dali and Von Gogh to BRASH: a case-based systematic literature review of digoxin induced BRASH syndrome.Future Cardiol. 2025 Mar;21(4):211-216. doi: 10.1080/14796678.2025.2466995. Epub 2025 Feb 15. Future Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39953848
Cited by
-
BRASH syndrome: A rare but reversible cause of sinus node dysfunction.HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2024 Mar 19;10(6):398-401. doi: 10.1016/j.hrcr.2024.03.005. eCollection 2024 Jun. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38983885 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- BRASH syndrome: bradycardia, renal failure, AV blockade, shock, and hyperkalemia. Farkas JD, Long B, Koyfman A, Menson K. J Emerg Med. 2020;59:216–223. - PubMed
-
- Effects of traumatic hypovolemic shock on renal function. Hayes DF, Werner MH, Rosenberg IK, Lucas CE, Westreich M, Bradley V. J Surg Res. 1974;16:490–497. - PubMed
-
- ACE inhibitors and ARBs: managing potassium and renal function. Momoniat T, Ilyas D, Bhandari S. Cleve Clin J Med. 2019;86:601–607. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
