Is Opioid-free Anesthesia Possible by Using Erector Spinae Plane Block in Spinal Surgery?
- PMID: 34786249
- PMCID: PMC8579823
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.18666
Is Opioid-free Anesthesia Possible by Using Erector Spinae Plane Block in Spinal Surgery?
Abstract
Objective: Erector spinae plane (ESP) block can be a method to be used for postoperative pain control in lumbar herniated disc operations. The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of erector spinae block in lumbar herniated disc operation on intraoperative and postoperative opioid consumption.
Methods: Sixty patients scheduled for lumbar herniated disc surgery were included in the study. Patients were randomized into two groups: ESP block and control. Ultrasound-guided ESP block with 20 ml 0.25% bupivacaine at the bilateral L3 vertebral level was applied preoperatively to all patients in the ESP group. Patients in both groups were provided with intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) device containing fentanyl for postoperative analgesia. Fentanyl consumption and visual analogue scale (VAS) score were recorded at 15 min, 1, 6, 12, and 24 hours postoperatively.
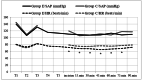
Results: Fentanyl consumption (group C: 59.3 ± 20.66, group E: 41.3 ± 21.61, p: 0,02) and VAS score (group C: VASm 4 (2-4), group E: 2 (2-4), p: 0.009) decreased with ESP block application at postoperative one hour. No difference was detected between the two groups in terms of fentanyl consumption and VAS score at 6, 12, and 24 hours postoperatively (p>0.05). The intraoperative heart rate of patients in the ESP group was lower than the control group (p<0.05).
Conclusion: ESP block decreases opioid consumption and VAS score at postoperative one hour in patients, and also patients who receive ESP block do not require intraoperative opioid administration.
Keywords: erector spinae plane block; intraoperative analgesia; lumbar herniated disc surgery; opioid consumption; postoperative analgesia.
Copyright © 2021, Taşkaldıran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- National trends in the surgical treatment for lumbar degenerative disc disease: United States, 2000 to 2009. Yoshihara H, Yoneoka D. Spine J. 2015;15:265–271. - PubMed
-
- Pain intensity on the first day after surgery: a prospective cohort study comparing 179 surgical procedures. Gerbershagen HJ, Aduckathil S, van Wijck AJ, Peelen LM, Kalkman CJ, Meissner W. Anesthesiology. 2013;118:934–944. - PubMed
-
- The role of multimodal analgesia in spine surgery. Kurd MF, Kreitz T, Schroeder G, Vaccaro AR. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25:260–268. - PubMed
-
- Analgesic therapy for major spine surgery. Puvanesarajah V, Liauw JA, Lo SF, Lina IA, Witham TF, Gottschalk A. Neurosurg Rev. 2015;38:407–418. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
