Cost-effective vital signs monitoring system for COVID-19 patients in smart hospital
- PMID: 34786323
- PMCID: PMC8585524
- DOI: 10.1007/s12553-021-00621-y
Cost-effective vital signs monitoring system for COVID-19 patients in smart hospital
Abstract
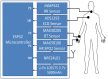
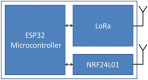
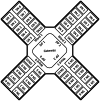
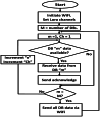
The lack of staffing during COVID-19 pandemic drives hospitals to expand their facilities in non-traditional settings to include centralized communication systems to monitor the vital signs of patients and predictive models to identify their health conditions. In this research, we have developed a microcontroller-based wireless vital signs monitoring system, which is able to measure the body temperature, heart rate, blood oxygen level, respiratory rate and Electrocardiogram of the patients. We managed to obtain a reliable but more affordable vital signs monitor with high mobility that can be implemented in large hospitals. The system satisfies the design considerations of medical centers in terms of size, cost, power consumption and simplicity in implementation. The developed system consists of a set of wearable sensor nodes, wireless communications infrastructure with multiple communications techniques to carry vital data from the patients to the management system that handles the patient's medical data, and a graphical user interface with a control system that enables the hospital staff to observe the status of all the patients and take the appropriate actions. The system was implemented using 40 sensor nodes, 4 distribution points and one gateway covering a hospital area of approximately 2500 m2. The system was tested and the measured percentage of lost packets is found to be less than 3.3% of those sent. During transmission, the current measured from the sensor node was 10.5 mA with a 3.3 V input voltage, which prolonged the operating time of the battery used.
Keywords: COVID-19; LoRa; Radio frequency; Smart hospitals; Vital signs; Wireless sensor network.
© IUPESM and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestWe have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Mshali H, Lemlouma T, Moloney M, Magoni D. A survey on health monitoring systems for health smart homes. Int J Ind Ergon. 2018;66:26–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2018.02.002. - DOI
-
- Pantelopoulos A, Bourbakis N. A Survey on wearable sensor-based systems for health monitoring and prognosis. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews). 2010;40(1):1–12. 10.1109/TSMCC.2009.2032660.
-
- Ortiz K, Davalos J, Eusebio E, Tucay D. IoT: Electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring system. Indones J Electr Eng Comput Sci. 2018;10(2):480–489. 10.11591/ijeecs.v10.i2.pp480-489.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
