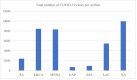
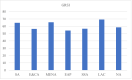
Policy Stringency, Handwashing and COVID-19 cases: Evidence from Global dataset
- PMID: 34786329
- PMCID: PMC8574075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hlpt.2021.100574
Policy Stringency, Handwashing and COVID-19 cases: Evidence from Global dataset
Abstract
Objective: : Since the COVID-19 pandemic, many governments globally have introduced policy measures to contain the spread of the virus. Popular COVID-19 containment measures include lockdowns of various forms (aggregated into government response stringency index [GRSI]) and handwashing (HWF). The effectiveness of these policy measures remains unclear in the academic literature. This study, therefore, examines the effect of government policy stringency and handwashing on total daily reported COVID-19 cases.
Method: : We use a comprehensive dataset of 176 countries to investigate the effect of government policy stringency and handwashing on daily reported COVID-19 cases. In this study, we apply the Lewbel (2012) two-stage least squares technique to control endogeneity.
Results: : Our results indicated that GRSI significantly contributes to the increase in the total and new confirmed cases of COVI-19. Sensitivity analyses revealed that the 1st, 4th, and 5th quintiles of GRIS significantly reduce total confirmed cases of COVID-19. Also, the result indicated that while the 1st quintile of GRIS contributes significantly to reducing the new confirmed cases of COVID-19, the 3rd, 4th, and 5th quintiles of GRSI contribute significantly to increasing the new confirmed cases of COVID-19. The results indicated that HWF reduces total and new confirmed cases of COVID-19; however, such effect is not robust to income and regional effects. Nonlinear analysis revealed that while GRSI has an inverted U-shaped relationship with total and new confirmed cases of COVID-19, HWF has a U-shaped relationship.
Conclusion: : We suggest that policymakers should focus on raising awareness and full engagement of all members of society in implementing public health policies rather than using stringent lockdown measures.
Keywords: COVID-19 Pandemic; Economic Development; Handwashing; Personal hygiene; Policy Stringency.
© 2021 Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
What is the relationship between government response and COVID-19 pandemics? Global evidence of 118 countries.Struct Chang Econ Dyn. 2021 Dec;59:98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.strueco.2021.08.007. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Struct Chang Econ Dyn. 2021. PMID: 35317309 Free PMC article.
-
Can Stringent Government Initiatives Lead to Global Economic Recovery Rapidly during the COVID-19 Epidemic?Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Mar 12;20(6):4993. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20064993. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36981902 Free PMC article.
-
Policy stringency and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal analysis of data from 15 countries.Lancet Public Health. 2022 May;7(5):e417-e426. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(22)00060-3. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Lancet Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35461592 Free PMC article.
-
Early policy actions and emergency response to the COVID-19 pandemic in Mongolia: experiences and challenges.Lancet Glob Health. 2020 Sep;8(9):e1234-e1241. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30295-3. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Lancet Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32711684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pandemic knowledge and regulation effectiveness: Evidence from COVID-19.J Comp Econ. 2022 Sep;50(3):768-783. doi: 10.1016/j.jce.2022.02.004. Epub 2022 Feb 23. J Comp Econ. 2022. PMID: 35221397 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hand-washing at critical times and associated factors among mothers of children under-five in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ital J Pediatr. 2024 Nov 6;50(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s13052-024-01801-y. Ital J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39501378 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating knowledge, awareness and associated water usage towards hand hygiene practices influenced by the current COVID-19 pandemic in Bangladesh.Groundw Sustain Dev. 2022 Nov;19:100848. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2022.100848. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Groundw Sustain Dev. 2022. PMID: 36164324 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 resilience index in European Union countries based on their risk and readiness scale.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 4;18(8):e0289615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289615. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37540717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organization WH. WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19-11 March 2020. 2020.
-
- Organization WH. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): situation report, 209. 2020.
-
- Stojkoski V, Utkovski Z, Jolakoski P, Tevdovski D, Kocarev L. arXiv preprint; 2020. The socio-economic determinants of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. arXiv:200407947.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources