BAIAP2L2 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma associated with the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 34786330
- PMCID: PMC8577457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbo.2021.100393
BAIAP2L2 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma associated with the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Abstract
Background: Osteosarcoma is the most common bone cancer that significantly affects the quality of life of patients. Studies have shown that overexpression of BAIAP2L2 elevates the proliferation and growth of some types of cancer cells. However, the role of BAIAP2L2 in osteosarcoma is unclear. This study aimed to investigate the functions of BAIAP2L2 in the development of osteosarcoma.
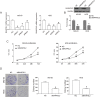
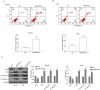
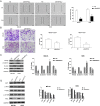
Methods: We used immunohistochemical and Western blot analysis to determine the expression levels of endogenic BAIAP2L2 in osteosarcoma cells. Cell counting kit-8 assay and colony formation assay were performed to investigate cell proliferation of tumor cells. Transwell assay was performed to detect cell migration. Flow cytometry assay was used to analyze cell apoptosis. The role of BAIAP2L2 in tumor growth was further explored in vivo.
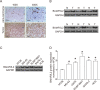
Results: We found that BAIAP2L2 was significantly upregulated in human osteosarcoma, and inhibition of BAIAP2L2 suppressed the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells. In addition, down-regulation of BAIAP2L2 could lead to osteosarcoma cancer cell apoptosis, inhibit cell migration and invasion, and induce the inactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. In addition, down-regulation of BAIAP2L2 inhibited tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion: In conclusion, down-regulation of BAIAP2L2 inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma associated with the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Keywords: BAIAP2L2; Combinational role; Osteosarcoma; Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BAIAP2L2 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via AKT/mTOR and Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;129:110414. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110414. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32570120
-
Down-regulation of PRR11 affects the proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.J Cancer. 2021 Sep 13;12(22):6656-6664. doi: 10.7150/jca.62491. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34659555 Free PMC article.
-
Ganoderma lucidum Exerts an Anticancer Effect on Human Osteosarcoma Cells via Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Integr Cancer Ther. 2019 Jan-Dec;18:1534735419890917. doi: 10.1177/1534735419890917. Integr Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 31855073 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of SOST Gene Silencing on Proliferation, Apoptosis, Invasion, and Migration of Human Osteosarcoma Cells Through the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Calcif Tissue Int. 2017 Jun;100(6):551-564. doi: 10.1007/s00223-016-0231-6. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Calcif Tissue Int. 2017. PMID: 28246931
-
Circ_0003732 promotes osteosarcoma progression through regulating miR-377-3p/CPEB1 axis and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Anticancer Drugs. 2022 Jan 1;33(1):e299-e310. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001206. Anticancer Drugs. 2022. PMID: 34407049
Cited by
-
Effect of traditional Chinese medicine in osteosarcoma: Cross-interference of signaling pathways and potential therapeutic targets.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jan 19;103(3):e36467. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036467. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38241548 Free PMC article.
-
Caudatin Inhibits the Proliferation, Invasion, and Glycolysis of Osteosarcoma Cells via the Wnt/β- Catenin Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Dec 23;2022:4026688. doi: 10.1155/2022/4026688. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36588592 Free PMC article.
-
BAIAP2L2 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and immune evasion of via targeting JAK1-mediated pathway and PD-L1 expression.Cancer Gene Ther. 2025 Apr;32(4):464-474. doi: 10.1038/s41417-025-00890-z. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Cancer Gene Ther. 2025. PMID: 40097840
-
Prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis and immunotherapeutic effects based on tryptophan metabolism-related genes.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Oct 10;22(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02730-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36217206 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of diagnostic biomarkers in prostate cancer-related fatigue by construction of predictive models and experimental validation.Br J Cancer. 2025 Feb;132(3):283-294. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02922-1. Epub 2024 Dec 15. Br J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39676131
References
-
- Ottaviani G., Jaffe N. Springer; 2009. The epidemiology of osteosarcoma. Pediatric and adolescent osteosarcoma; pp. 3–13. - PubMed
-
- Chung E.B., Enzinger F.M. Extraskeletal osteosarcoma. Cancer. 1987;60(5):1132–1142. - PubMed
-
- Longhi A., Errani C., De Paolis M., Mercuri M., Bacci G. Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: state of the art. Cancer treatment reviews. 2006;32(6):423–436. - PubMed
-
- Bassin E.B., Wypij D., Davis R.B., Mittleman M.A. Age-specific fluoride exposure in drinking water and osteosarcoma (United States) Cancer Causes & Control. 2006;17(4):421–428. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

