Efficacy of subcutaneous immunotherapy for patients with asthma and allergic rhinitis in Korea: effect on eosinophilic inflammation
- PMID: 34786373
- PMCID: PMC8563102
- DOI: 10.5415/apallergy.2021.11.e43
Efficacy of subcutaneous immunotherapy for patients with asthma and allergic rhinitis in Korea: effect on eosinophilic inflammation
Abstract
Background: Atopic asthma (AA) and allergic rhinitis (AR) are often seen as comorbidities and specific immunotherapy (SIT) is considered evidence-based treatment for them both.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of multiallergen subcutaneous SIT (SCIT) in reducing nasal and sputum eosinophilia, symptom scores, and impaired lung function in Korean pediatric patients with AR and AA.
Methods: Children aged 6-15 years with a documented history of bronchial asthma and seasonal/perennial AR were recruited then randomly selected to 1 of 2 groups: "immunotherapy group" (inhaled corticosteroids [ICS] and short-acting beta2-agonist [SABA] + subcutaneous injection of standardized extracts of up to 4 allergens [n = 53]) or "drug only group" (ICS and SABA only [n = 19]). All data were collected retrospectively.
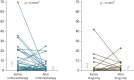
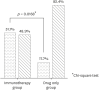
Results: Comparing the 2 treatment groups, the immunotherapy group showed a significantly (p = 0.006) greater reduction in nasal eosinophilia over the 3-year treatment period. Only the immunotherapy group exhibited a significant reduction in sputum eosinophilia over the 3-year treatment period (p = 0.003). Fifty-one point one percent of patients in the immunotherapy group showed significant improvement in the methacholine challenge test negative conversion rate compared to only 17.65% in the drug only group (p = 0.0168). There were significantly greater improvements in symptom scores in the immunotherapy group compared to the drug only group. For all allergens tested, only house dust mite reactivity changed significantly over the treatment period and only in the immunotherapy group (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus [p < 0.0001] and Dermatophagoides farina [p = 0.035]).
Conclusion: SCIT was associated with greater improvements in lung function and bronchial hyperresponsiveness and reductions in nasal and sputum eosinophilia and allergen reactivity. Changes in symptom scores were also much greater in patients receiving SCIT when compared to those who did not receive it. Korean children with AA and AR respond well to long-term multiallergen SCIT.
Keywords: Allergen immunotherapy; Child; Desensitization; Eosinophilia.
Copyright © 2021. Asia Pacific Association of Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bousquet J, Schünemann HJ, Samolinski B, Demoly P, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bachert C, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA): achievements in 10 years and future needs. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:1049–1062. - PubMed
-
- Nelson HS. In: Middleton's allergy. 7th ed. Adkinson NF Jr, Bochner BS, Busse WW, Holgate ST, Lemanske RF Jr, Simons FER, editors. Atlanta (GA): Elsevier; 2008. Immunotherapy for Inhalant Allergens; pp. 1657–1677.
-
- Atkins D, Leung DYM. In: Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 18th ed. Kliegman RM, Behrman RE, Jenson HB, Stanton BF, editors. Philadelphia (PA): Saunders; 2007. Principles of treatment of allergic disease; pp. 942–949.
-
- Akdis M, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:780–791. - PubMed
-
- Ciprandi G, Cirillo I, Vizzaccaro A, Milanese M, Tosca MA. Airway function and nasal inflammation in seasonal allergic rhinitis and asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004;34:891–896. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
