C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand 1/receptor 1 regulates the M1 polarization and chemotaxis of macrophages after hypoxia/reoxygenation injury
- PMID: 34786544
- PMCID: PMC8579018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cdtm.2021.05.001
C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand 1/receptor 1 regulates the M1 polarization and chemotaxis of macrophages after hypoxia/reoxygenation injury
Abstract
Background: Macrophages play an important role in renal ischemia reperfusion injury, but the functional changes of macrophages under hypoxia/reoxygenation and the related mechanism are unclear and need to be further clarified.
Methods: The effects of hypoxia/reoxygenation on functional characteristics of RAW264.7 macrophages were analyzed through the protein expression detection of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α and CD80, anti-inflammatory factors ARG-1 and CD206. The functional implications of C-X3-C motif chemokine receptor 1(CX3CR1) down-regulation in hypoxic macrophages were explored using small interfering RNA technology. Significance was assessed by the parametric t-test or nonparametric Mann-Whitney test for two group comparisons, and a one-way ANOVA or the Kruskal-Wallis test for multiple group comparisons.
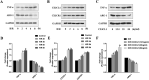
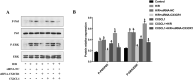
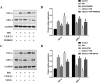
Results: Hypoxia/reoxygenation significantly increased the protein expression of M1-related pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α, CD80 and chemokine C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand 1 (CX3CL1)/CX3CR1 and inhibited the protein expression of M2-related anti-inflammatory factors ARG-1 and CD206 in a time-dependent manner in RAW264.7 cells. However, the silencing of CX3CR1 in RAW264.7 cells using specific CX3CR1-siRNA, significantly attenuated the increase in protein expression of TNF-α (P < 0.05) and CD80 (P < 0.01) and the inhibition of ARG-1 (P < 0.01) and CD206 (P < 0.01) induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation. In addition, we also found that hypoxia/reoxygenation could significantly enhance the migration (2.2-fold, P < 0.01) and adhesion capacity (1.5-fold, P < 0.01) of RAW264.7 macrophages compared with the control group, and CX3CR1-siRNA had an inhibitory role (40% and 20% reduction, respectively). For elucidating the mechanism, we showed that the phosphorylation levels of ERK (P < 0.01) and the p65 subunit of NF-κB (P < 0.01) of the RAW264.7 cells in the hypoxic/reoxygenation group were significantly increased, which could be attenuated by down-regulation of CX3CR1 expression (P < 0.01, both). ERK inhibitors also significantly blocked the effects of hypoxic/reoxygenation on the protein expression of M1-related pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α, CD80 and M2-related anti-inflammatory factors ARG-1 and CD206. Moreover, we found that conditioned medium from polarized M1 macrophages induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation, notably increased the degree of apoptosis of hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced TCMK-1 cells, and promoted the protein expression of pro-apoptotic proteins bax (P < 0.01) and cleaved-caspase 3 (P < 0.01) and inhibited the expression of anti-apoptotic protein bcl-2 (P < 0.01), but silencing CX3CR1 in macrophages had a protective role. Finally, we also found that the secretion of soluble CX3CL1 in RAW264.7 macrophages under hypoxia/reoxygenation was significantly increased.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that hypoxia/reoxygenation could promote M1 polarization, cell migration, and adhesion of macrophages, and that polarized macrophages induce further apoptosis of hypoxic renal tubular epithelial cells by regulating of CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand 1/receptor 1; Hypoxia/Reoxygenation; Macrophages; Phenotypic polarization.
© 2021 Chinese Medical Association. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co. Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
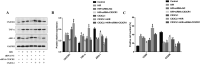


Similar articles
-
CX3CR1 deficiency exacerbates immune-mediated hepatitis by increasing NF-κB-mediated cytokine production in macrophage and T cell.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023 Jan;248(2):117-129. doi: 10.1177/15353702221128573. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023. PMID: 36426712 Free PMC article.
-
CX3CL1/CX3CR1 interaction protects against lipotoxicity-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating macrophage migration and M1/M2 status.Metabolism. 2022 Nov;136:155272. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155272. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Metabolism. 2022. PMID: 35914622
-
CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in human nucleus pulpous cells via M2 macrophage polarization.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Jun 7;26(1):359. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12058. eCollection 2023 Jul. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37324510 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-specific Role of CX3CR1 Expressing Immune Cells and Their Relationships with Human Disease.Immune Netw. 2018 Jan 25;18(1):e5. doi: 10.4110/in.2018.18.e5. eCollection 2018 Feb. Immune Netw. 2018. PMID: 29503738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monocytes and dendritic cells in a hypoxic environment: Spotlights on chemotaxis and migration.Immunobiology. 2008;213(9-10):733-49. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2008.07.031. Epub 2008 Sep 21. Immunobiology. 2008. PMID: 18926289 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of tubastatin A on NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages under hypoxia/reoxygenation conditions.World J Emerg Med. 2024;15(4):289-296. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.059. World J Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39050221 Free PMC article.
-
CX3CL1 (Fractalkine)-CX3CR1 Axis in Inflammation-Induced Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 25;25(9):4679. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094679. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CX3CR1 regulates the development of renal interstitial fibrosis through macrophage polarization.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Jul 28;48(7):957-966. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220601. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37724398 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

