All hands on deck: SARS-CoV-2 proteins that block early anti-viral interferon responses
- PMID: 34786565
- PMCID: PMC8588586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crviro.2021.100015
All hands on deck: SARS-CoV-2 proteins that block early anti-viral interferon responses
Abstract
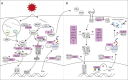
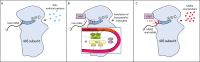
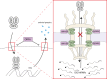
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is responsible for the current pandemic coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19). Like other pathogens, SARS-CoV-2 infection can elicit production of the type I and III interferon (IFN) cytokines by the innate immune response. A rapid and robust type I and III IFN response can curb viral replication and improve clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection. To effectively replicate in the host, SARS-CoV-2 has evolved mechanisms for evasion of this innate immune response, which could also modulate COVID-19 pathogenesis. In this review, we discuss studies that have reported the identification and characterization of SARS-CoV-2 proteins that inhibit type I IFNs. We focus especially on the mechanisms of nsp1 and ORF6, which are the two most potent and best studied SARS-CoV-2 type I IFN inhibitors. We also discuss naturally occurring mutations in these SARS-CoV-2 IFN antagonists and the impact of these mutations in vitro and on clinical presentation. As SARS-CoV-2 continues to spread and evolve, researchers will have the opportunity to study natural mutations in IFN antagonists and assess their role in disease. Additional studies that look more closely at previously identified antagonists and newly arising mutants may inform future therapeutic interventions for COVID-19.
Keywords: 3CLpro, 3-chymotrypsin like protease; COVID-19, coronavirus disease of 2019; IFN, interferon; IFNAR, interferon alpha/beta receptor; IFNLR, interferon lambda receptor; IRF, interferon response factor; ISRE, interferon stimulated response element; Immune evasion; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; MDA-5, melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; ORF, open reading frame; ORF6; PLpro, papain-like protease; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible gene I; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2, SARS coronavirus 2; SRP, signal recognition particle; STAT, signal transducer and regulator of transcription; SeV, Sendai virus; TAB1, TGF-beta activated kinase 1 binding protein 1; TAK1, TGF-beta activated kinase 1; TBK1, TANK-binding kinase 1; TLR, toll-like receptor; TRIF, TIR domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon beta; Type I interferon; UTR, untranslated region; eIF, eukaryotic initiation factor; nsp, non-structural protein; nsp1.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Marta M. Gaglia reports financial support was provided by American Lung Association.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evasion of Type I Interferon by SARS-CoV-2.Cell Rep. 2020 Oct 6;33(1):108234. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108234. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32979938 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of IRF-3-dependent innate immunity by the papain-like protease domain of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 2;282(44):32208-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704870200. Epub 2007 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17761676 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-Cov2 acute and post-active infection in the context of autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases.J Transl Autoimmun. 2022;5:100154. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2022.100154. Epub 2022 Apr 12. J Transl Autoimmun. 2022. PMID: 35434592 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3270-85. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.979640. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and functions of SARS-CoV-2 proteins in host immune evasion.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 8;13:940756. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.940756. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36003396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 non-structural proteins 1 and 15 proteins mediate antiviral immune evasion.Curr Res Virol Sci. 2022;3:100021. doi: 10.1016/j.crviro.2022.100021. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Curr Res Virol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35187506 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Role of Interferons in Viral and Bacterial Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 14;24(12):10115. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210115. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nsp1 proteins of human coronaviruses HCoV-OC43 and SARS-CoV2 inhibit stress granule formation.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Dec 19;18(12):e1011041. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011041. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36534661 Free PMC article.
-
Co-evolution of SARS-CoV-2 variants and host immune response trajectories underlie COVID-19 pandemic to epidemic transition.iScience. 2023 Oct 27;26(12):108336. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108336. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38025778 Free PMC article.
-
Nsp16 shields SARS-CoV-2 from efficient MDA5 sensing and IFIT1-mediated restriction.EMBO Rep. 2022 Dec 6;23(12):e55648. doi: 10.15252/embr.202255648. Epub 2022 Oct 26. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 36285486 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
