Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Endoxifen for Tamoxifen Precision Dosing: Feasible in Patients with Hormone-Sensitive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 34786650
- PMCID: PMC8975771
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-021-01077-z
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Endoxifen for Tamoxifen Precision Dosing: Feasible in Patients with Hormone-Sensitive Breast Cancer
Abstract
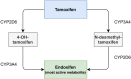
Background: Endoxifen is the most important active metabolite of tamoxifen. Several retrospective studies have suggested a minimal or threshold endoxifen systemic concentration of 14-16 nM is required for a lower recurrence rate. The aim of this study was to investigate the feasibility of reaching a predefined endoxifen level of ≥ 16 nM (5.97 ng/mL) over time using therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM).
Methods: This prospective open-label intervention study enrolled patients who started treatment with a standard dose of tamoxifen 20 mg once daily for early breast cancer. An outpatient visit was combined with a TDM sample at 3, 4.5, and 6 months after initiation of the tamoxifen treatment. The tamoxifen dose was escalated to a maximum of 40 mg if patients had an endoxifen concentration < 16 nM. The primary endpoint of the study was the percentage of patients with an endoxifen level ≥ 16 nM at 6 months after the start of therapy compared with historical data, in other words, 80% of patients with endoxifen levels ≥ 16 nM with standard therapy.
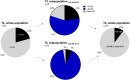
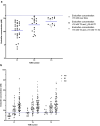
Results: In total, 145 patients were included. After 6 months, 89% of the patients had endoxifen levels ≥ 16 nM, compared with a literature-based 80% of patients with endoxifen levels ≥ 16 nM at baseline (95% confidence interval 82-94; P = 0.007). In patients with an affected CYP2D6 allele, it was not always feasible to reach the predefined endoxifen level of ≥ 16 nM. No increase in tamoxifen-related adverse events was reported after dose escalation.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that it is feasible to increase the percentage of patients with endoxifen levels ≥ 16 nM using TDM. TDM is a safe strategy that offers the possibility of nearly halving the number of patients with endoxifen levels < 16 nM.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
C. Louwrens Braal, Agnes Jager, Esther Oomen–de Hoop, Justin D. Westenberg, Koen M.W.T. Lommen, Peter de Bruijn, Mijntje M. Vastbinder, Quirine C. van Rossum–Schornagel, Martine F. Thijs–Visser, Robbert J. van Alphen, Liesbeth E.M. Struik, Hanneke J.M. Zuetenhorst, Ron H.J. Mathijssen, and Stijn L.W. Koolen have no potential conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dose Escalation of Tamoxifen in Patients with Low Endoxifen Level: Evidence for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring-The TADE Study.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 1;22(13):3164-71. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1470. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26847054 Clinical Trial.
-
Tamoxifen Dose Escalation in Patients With Diminished CYP2D6 Activity Normalizes Endoxifen Concentrations Without Increasing Toxicity.Oncologist. 2016 Jul;21(7):795-803. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0480. Epub 2016 May 25. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 27226358 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of model-informed precision dosing for tamoxifen therapy in patients with breast cancer: A prospective intervention study.Breast. 2025 Feb;79:103880. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2025.103880. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Breast. 2025. PMID: 39813819 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics of tamoxifen and endoxifen.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Jun;12(6):523-536. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2019.1610390. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31008668 Review.
-
Individualization of tamoxifen therapy: much more than just CYP2D6 genotyping.Cancer Treat Rev. 2015 Mar;41(3):289-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015. PMID: 25618289 Review.
Cited by
-
Variation in human gut microbiota impacts tamoxifen pharmacokinetics.mBio. 2025 Jan 8;16(1):e0167924. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01679-24. Epub 2024 Nov 25. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39584836 Free PMC article.
-
Endoxifen Concentration Is Associated with Recurrence-Free Survival in Hormone-Sensitive Breast Cancer Patients.Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jan;57(1):140-149. doi: 10.4143/crt.2023.1285. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 38901825 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics of Tamoxifen and Its Major Metabolites and the Effect of the African Ancestry Specific CYP2D6*17 Variant on the Formation of the Active Metabolite, Endoxifen.J Pers Med. 2023 Jan 31;13(2):272. doi: 10.3390/jpm13020272. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36836506 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of probenecid on endoxifen systemic exposure in breast cancer patients on adjuvant tamoxifen treatment.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022 Mar 17;14:17588359221081075. doi: 10.1177/17588359221081075. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35321309 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of endoxifen-guided tamoxifen dose reductions on endocrine side-effects in patients with primary breast cancer.ESMO Open. 2023 Feb;8(1):100786. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.100786. Epub 2023 Feb 6. ESMO Open. 2023. PMID: 36753991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cuzick J, Powles T, Veronesi U, Forbes J, Edwards R, Ashley S. Overview of the main outcomes in breast-cancer prevention trials. Lancet. 2003;361(9354):296–300. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group Trialists' Collaborative Group. Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 1998;351(9114):1451–1467. - PubMed
-
- Osborne CK. Tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(22):1609–1618. - PubMed
-
- Burstein HJ, Lacchetti C, Anderson H, Buchholz TA, Davidson NE, Gelmon KA. Adjuvant endocrine therapy for women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: ASCO clinical practice guideline focused update. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(5):423–438. - PubMed
-
- Visvanathan K, Fabian CJ, Bantug E, Brewster AM, Davidson NE, DeCensi A. Use of endocrine therapy for breast cancer risk reduction: ASCO clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(33):3152–3165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

