Evaluation of Protocols of Controlled Ovarian Stimulation in Obtaining Mature Oocytes (MII): Retrospective Study on Assisted Reproductive Technology Procedures
- PMID: 34786902
- PMCID: PMC9355430
- DOI: 10.5935/1518-0557.20210077
Evaluation of Protocols of Controlled Ovarian Stimulation in Obtaining Mature Oocytes (MII): Retrospective Study on Assisted Reproductive Technology Procedures
Abstract
Objective: To understand which of the controlled ovarian stimulation (COS) protocols used in different patients are associated with greater amounts of oocytes retrieved.
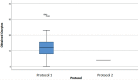
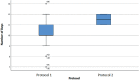
Methods: The study population was divided into three groups, considering AMH and AFC to obtain the Ovarian Response Predictor Index (ORPI); they were grouped into: G1-Low Reserve (ORPI <0.5); G2-Normal Reserve (ORPI:0.5-0.9); and G3-High Reserve (ORPI≥0.9). 246 cycles were selected in which COS was used: recombinant FSH - follitropin alfa or beta (Protocol 1) or corifollitropin alfa (Protocol 2), both associated with urinary HMG and the GnRH antagonist, with the trigger performed using recombinant hCG or GnRH agonist.
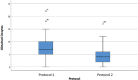
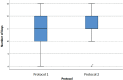
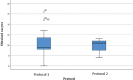
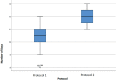
Results: The number of oocytes obtained was higher in protocol 1 in all groups, with higher counts seen in G1 than in G2 or G3. The number of days required in COS for protocol 2 was greater than for protocol 1 in all groups. The total dose of recombinant FSH alfa or beta / urinary HMG used in protocol 1 was inversely proportional to the ovarian reserve. The lower the ORPI, the greater the average number of international units administered. In protocol 2, there was a need to supplement with higher doses of urinary HMG when compared to protocol 1. The dosage of the GnRH antagonist was dependent on the number of COS days until the trigger was used. In obtaining MII oocytes, the percentages were similar regardless of the trigger used.
Conclusions: The use of follitropin leads to greater numbers of retrieved oocytes than corifollitropin alfa in all ORPIs. The dose of recombinant FSH used with urinary HMG increases inversely proportional to the ORPI value. The fixed dose of recombinant FSH deposit requires a sharp increase in the dose of urinary HMG.
Keywords: anti-Müllerian hormone; antral follicle count; assisted reproductive technology; controlled ovarian stimulation; infertility.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there was no support from any organization for the submitted paper, no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted study and no other relationships or activities that might appear to have influenced the submitted study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Corifollitropin alfa compared to daily rFSH or HP-HMG in GnRH antagonist controlled ovarian stimulation protocol for patients undergoing assisted reproduction.JBRA Assist Reprod. 2017 Jun 1;21(2):67-69. doi: 10.5935/1518-0557.20170017. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28609269 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of domestic highly purified urinary follicle stimulating hormone on outcomes of in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer in controlled ovarian stimulation].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Nov;48(11):838-42. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24444561 Chinese.
-
Large, comparative, randomized double-blind trial confirming noninferiority of pregnancy rates for corifollitropin alfa compared with recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone in a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist controlled ovarian stimulation protocol in older patients undergoing in vitro fertilization.Fertil Steril. 2015 Jul;104(1):94-103.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.04.018. Epub 2015 May 21. Fertil Steril. 2015. PMID: 26003273 Clinical Trial.
-
Corifollitropin alfa: a review of its use in controlled ovarian stimulation for assisted reproduction.BioDrugs. 2011 Aug 1;25(4):243-54. doi: 10.2165/11206890-000000000-00000. BioDrugs. 2011. PMID: 21815699 Review.
-
Ovarian Stimulation Protocol in IVF: An Up-to-Date Review of the Literature.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016;17(4):303-15. doi: 10.2174/1389201017666160118103147. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26775651 Review.
Cited by
-
The quality of human eggs and its pre-IVF incubation.Reprod Med Biol. 2025 May 2;24(1):e12652. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12652. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Reprod Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40321658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Biljan MM, Mahutte NG, Dean N, Hemmings R, Bissonnette F, Tan SL. Effects of pretreatment with an oral contraceptive on the time required to achieve pituitary suppression with gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues and on subsequent implantation and pregnancy rates. Fertil Steril. 1998;70:1063–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0015-0282(98)00333-1. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

