Circular RNA circ_0048764 promotes the development of breast cancer by regulating microRNA-1296-5p/tripartite motif containing 14 axis
- PMID: 34787066
- PMCID: PMC8973759
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1995990
Circular RNA circ_0048764 promotes the development of breast cancer by regulating microRNA-1296-5p/tripartite motif containing 14 axis
Abstract
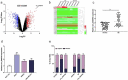
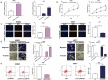
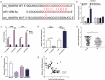
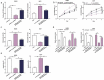
Breast cancer (BC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in females. Circular RNA (circRNA), as reported, is involved in the progression of BC. This work focuses on clarifying the biological function of circ_0048764 in BC and its hidden mechanism. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed to detect the expressions of circ_0048764, microRNA-1296-5p (miR-1296-5p), and tripartite motif containing 14 (TRIM14) in BC tissues and cell lines. Besides, the status of proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of BC cells was probed by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), EdU, transwell and flow cytometry assays. Western blot was adopted to examine the level of TRIM14 protein in BC cells. In addition, dual-luciferase reporter gene assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay were conducted to corroborate the targeting relationships between miR-1296-5p and circ_0048764 or TRIM14. It was revealed that circ_0048764 expression was remarkably up-regulated in BC tissues and cells, and circ_0048764 expression was associated with TNM stage and tumor size. Functionally, overexpression of circ_0048764 significantly promoted BC cell proliferative, migrative and invasive abilities and inhibited apoptosis, while circ_0048764 knockdown exerted the opposite effects. Mechanistically, circ_0048764 directly targeted miR-1296-5p and could negatively modulate its expression in BC cells. Besides, miR-1296-5p could reverse the influence of circ_0048764 on BC viability, migration, invasion and apoptosis. Moreover, TRIM14 was confirmed to be a downstream target of miR-1296-5p. Circ_0048764 positively regulated TRIM14 expression in BC cells via targeting miR-1296-5p. Collectively, it is concluded that circ_0048764 promotes the development of BC via modulating the miR-1296-5p/TRIM14 axis.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Trim14; circ_0048764; miR-1296-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Guanghui R, Xiaoyan H, Shuyi Y, et al. An efficient or methodical review of immunotherapy against breast cancer. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2019. Aug;33(8):e22339. - PubMed
-
- Liang Y, Zhang H, Song X, et al. Metastatic heterogeneity of breast cancer: molecular mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. Feb;60:14–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
