Interference of KLF9 relieved the development of gestational diabetes mellitus by upregulating DDAH2
- PMID: 34787071
- PMCID: PMC8805879
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2005929
Interference of KLF9 relieved the development of gestational diabetes mellitus by upregulating DDAH2
Retraction in
-
Statement of Retraction: Interference of KLF9 relieved the development of gestational diabetes mellitus by upregulating DDAH2.Bioengineered. 2024 Dec;15(1):2299612. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2024.2299612. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Bioengineered. 2024. PMID: 38376882 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
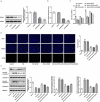
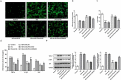
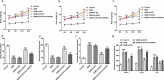
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a situation where glucose intolerance is found in pregnant women without a previous diagnosis of diabetes. The role of Kruppel-like factor 9 (KLF9) has not been investigated in GDM, which constituted the aim of our study. HTR8/SVneo cells were induced by high glucose (HG) and pregnant mice were treated with streptozocin (STZ) to establish GDM model in vitro and in vivo, respectively. The expression level of KLF9 was detected by real-time PCR, immunohistochemical staining, and Western blot. Cell viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress were investigated by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), TUNEL, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and oxidative stress detection kits, respectively. The interaction of KLF9 with dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 2 (DDAH2) was predicted by bioinformatic tools and confirmed by luciferase reporter assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). The expression of KLF9 was increased in the placental tissues of GDM patients and HG-induced HTR8/SVneo cells. Silencing of KLF9 increased cell viability, reduced cell apoptosis, and suppressed inflammation and oxidative stress in HG-induced HTR8/SVneo cells. KLF9 could bind to DDAH2 promoter and negatively regulate DDAH2 expression. Inhibition of DDAH2 partly weakened the effects of KLF9 silencing on cell apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress. The suppressive effects of KLF9 silencing on blood glucose and insulin concentration in vivo were also abolished by DDAH2 knockdown. In conclusion, we provided evidence that interference of KLF9 could hinder the development of GDM by alleviating cell apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress through upregulating DDAH2, which might instruct the targeting therapies against GDM.Abbreviations: KLF9: Kruppel-like factor 9; DDAH2: dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 2 ; GDM: gestational diabetes mellitus; ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; CCK-8: cell counting kit-8; ChIP: chromatin immunoprecipitation; sh: short hairpin; HG: high glucose; PBS: phosphate-buffered saline; DAPI: 4, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; ROS: reactive oxygen species; MDA: malondialdehyde; SOD: superoxide dismutase; wt: wild-type; mut: mutant.
Keywords: DDAH2; KLF9; gestational diabetes mellitus; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
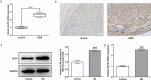
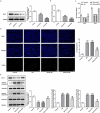
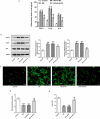
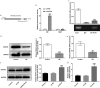
Similar articles
-
miR-134-5p promotes inflammation and apoptosis of trophoblast cells via regulating FOXP2 transcription in gestational diabetes mellitus.Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):319-330. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2001219. Bioengineered. 2022. Retraction in: Bioengineered. 2024 Dec;15(1):2299586. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2024.2299586. PMID: 34969354 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Nesfatin-1 alleviates high glucose/high lipid-induced injury of trophoblast cells during gestational diabetes mellitus.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12789-12799. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2001205. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34895049 Free PMC article.
-
High glucose regulates the cells dysfunction of human trophoblast HTR8/SVneo cells by downregulating GABRP expression.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2024 Oct;33(10):1123-1130. doi: 10.17219/acem/174347. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38197563
-
The Effect of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants Treatment on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Outcome: A Scoping Review.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Dec;82(4):3003-3013. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01417-3. Epub 2024 Jul 13. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 39003362
-
The impact of environmental and dietary exposure on gestational diabetes mellitus: a comprehensive review emphasizing the role of oxidative stress.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 2;16:1393883. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1393883. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40241987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The protective effects of butorphanol tartrate against homocysteine-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):7209-7220. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2037953. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35245993 Free PMC article.
-
Src-homology domain 2 containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) directly binds to proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src (c-Src) and promotes the transcriptional activation of connexin 43 (Cx43).Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13534-13543. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2079252. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35659197 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent Fasting-Improved Glucose Homeostasis Is Not Entirely Dependent on Caloric Restriction in db/db Male Mice.Diabetes. 2024 Jun 1;73(6):864-878. doi: 10.2337/db23-0157. Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38502858 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease: an integrative bioinformatics and machine learning analysis reveals glutamine metabolism-associated gene biomarkers.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Jan 28;26(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00852-z. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39875978 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide screening of m6A profiling of cutaneous wound healing in diabetic mice.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jan 22;51(1):175. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09089-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38252224
References
-
- Mack LR, Tomich PG.. Gestational diabetes: diagnosis, classification, and clinical care. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2017;44(2):207–217. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation Gestational Diabetes . [cited 2018 10 Dec].
-
- McIntyre HD, Catalano P, Zhang C, et al. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):47. - PubMed
-
- Xing J, Jia Z, Xu Y, et al. KLF9 (Kruppel Like Factor 9) induced PFKFB3 (6-Phosphofructo-2-Kinase/Fructose-2, 6-Biphosphatase 3) downregulation inhibits the proliferation, metastasis and aerobic glycolysis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):7563–7576. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
