Experimental study of fat derived pellets promoting wound healing in rats
- PMID: 34787072
- PMCID: PMC8810055
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2000257
Experimental study of fat derived pellets promoting wound healing in rats
Abstract
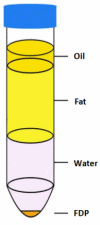
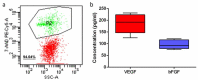
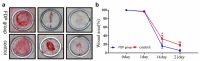
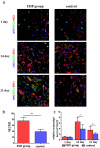
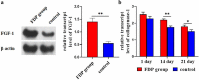
To observe the effect of fat-derived pellets (FDP) on wound healing in rats, the inguinal fat of rats was obtained, and the FDP were obtained after centrifugation. The cell activity and growth factor secretion of FDP were measured. The wounds in rats were created, and FDP was used to treat the wounds of rats. The phenotype of macrophages and the expression of angiogenic factors expression in wounds were measured. The cell viability in FDP remains in high level after centrifugation and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (bFGF) from FDP was observed in vitro. The FDP significantly promoted the wound healing of rats compared with that in control groups. Moreover, the expression of M2 macrophages and VEGF in FDP group were significantly higher than that in the control group. FDP is a kind of stem cell product, which can be obtained from adipose tissue by physical centrifugation. The cytotherapeutic effect of FDP makes it a promising product for wound healing in clinics.
Keywords: Stem cell; growth factors; macrophages; physical method; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Effects of hypoxia-pretreated rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells conditioned medium on wound healing of rats with full-thickness defects].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020 Sep 20;36(9):803-812. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200508-00258. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32972065 Chinese.
-
[Effects of arnebia root oil on wound healing of rats with full-thickness skin defect and the related mechanism].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2017 Sep 20;33(9):562-567. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2017.09.008. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28926878 Chinese.
-
[Effects and mechanism of rat epidermal stem cells treated with exogenous vascular endothelial growth factor on healing of deep partial-thickness burn wounds in rats].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020 Mar 20;36(3):195-203. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20191125-00441. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32241045 Chinese.
-
[Stem cells and growth factors in wound healing].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015 Jan 2;69:874-85. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1162989. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015. PMID: 26270514 Review. Polish.
-
Implications of Extracellular Matrix Production by Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells for Development of Wound Healing Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 31;18(6):1167. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061167. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28561757 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage plasticity: signaling pathways, tissue repair, and regeneration.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 1;5(8):e658. doi: 10.1002/mco2.658. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39092292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carboxymethyl chitosan-grafted polyvinylpyrrolidone-iodine microspheres for promoting the healing of chronic wounds.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):8735-8746. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2054911. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35322745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walter MN, Wright KT, Fuller HR, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium accelerates skin wound healing: an in vitro study of fibroblast and keratinocyte scratch assays[J]. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(7):1271–1281. - PubMed
-
- Yoon BS, Moon JH, Jun EK, et al. Secretory profiles and wound healing effects of human amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(6):887–902. - PubMed
-
- Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies[J]. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
