EDTA and Taurolidine Affect Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence In Vitro-Impairment of Secretory Profile and Biofilm Production onto Peritoneal Dialysis Catheters
- PMID: 34787464
- PMCID: PMC8597648
- DOI: 10.1128/Spectrum.01047-21
EDTA and Taurolidine Affect Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence In Vitro-Impairment of Secretory Profile and Biofilm Production onto Peritoneal Dialysis Catheters
Abstract
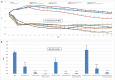
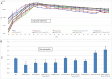
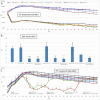
Peritoneal catheter-associated biofilm infection is reported to be the main cause of refractory peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients. The application of antimicrobial lock therapy, based on results on central venous catheters, may be a promising option for treatment of biofilm-harboring peritoneal catheters. This study investigated the effects of two lock solutions, EDTA and taurolidine, on an in vitro model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm-related peritoneal catheter infection. Silicone peritoneal catheters were incubated for 24 h with a bioluminescent strain of P. aeruginosa. Then, serial dilutions of taurolidine and/or EDTA were applied (for 24 h) once or twice onto the contaminated catheters, and P. aeruginosa viability/persistence were evaluated in real time up to 120 h using a Fluoroskan reader. On selected supernatants, high-performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) analysis was performed to measure the production of autoinducers (AI), phenazines, and pyocyianines. Taurolidine alone or in combination with EDTA caused a significant decrease of bacterial load and biofilm persistence on the contaminated catheters. The treatment did not lead to the sterilization of the devices, yet it resulted in a substantial destructuration of the catheter-associated P. aeruginosa biofilm. HPLC-MS analysis showed that the treatment of biofilm-harboring catheters with taurolidine and EDTA also affected the secretory activity of the pathogen. EDTA and taurolidine affect P. aeruginosa biofilm produced on peritoneal catheters and profoundly compromise the microbial secretory profile. Future studies are needed to establish whether such lock solutions can be used to render peritoneal catheter-related infections more susceptible to antibiotic treatment. IMPORTANCE An in vitro model allows studies on the mechanisms by which the lock solutions exert their antimicrobial effects on catheter-associated biofilm, thus providing a better understanding of the management of devise-associated infections.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; biofilm; lock solutions; peritoneal dialysis catheters.
Figures

References
-
- Htay H, Cho Y, Pascoe EM, Darssan D, Nadeau-Fredette A-C, Hawley C, Clayton PA, Borlace M, Badve SV, Sud K, Boudville N, McDonald SP, Johnson DW. 2017. Multicenter registry analysis of center characteristics associated with technique failure in patients on incident peritoneal dialysis. CJASN 12:1090–1099. doi: 10.2215/CJN.12321216. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Sahlawi M, Wilson G, Stallard B, Manera KE, Tong A, Pisoni RL, Fuller DS, Cho Y, Johnson DW, Piraino B, Schreiber MJ, Boudville NC, Teitelbaum I, Perl J. 2020. Peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis outcomes reported in trials and observational studies: a systematic review. 2020. Perit Dial Int 40:132–140. doi: 10.1177/0896860819893810. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

