LncRNA NEAT1 Recruits SFPQ to Regulate MITF Splicing and Control RPE Cell Proliferation
- PMID: 34787639
- PMCID: PMC8606808
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.62.14.18
LncRNA NEAT1 Recruits SFPQ to Regulate MITF Splicing and Control RPE Cell Proliferation
Abstract
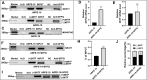
Purpose: Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell proliferation is precisely regulated to maintain retinal homoeostasis. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF), a critical transcription factor in RPE cells, has two alternatively spliced isoforms: (+)MITF and (-)MITF. Previous work has shown that (-)MITF but not (+)MITF inhibits RPE cell proliferation. This study aims to investigate the role of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) in regulating MITF splicing and hence proliferation of RPE cells.
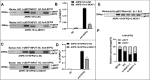
Methods: Mouse RPE, primary cultured mouse RPE cells, and different proliferative human embryonic stem cell (hESC)-RPE cells were used to evaluate the expression of (+)MITF, (-)MITF, and NEAT1 by reverse-transcription PCR (RT-PCR) or quantitative RT-PCR. NEAT1 was knocked down using specific small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). Splicing factor proline- and glutamine-rich (SFPQ) was overexpressed with the use of lentivirus infection. Cell proliferation was analyzed by cell number counting and Ki67 immunostaining. RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) was used to analyze the co-binding between the SFPQ and MITF or NEAT1.
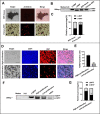
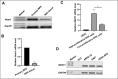
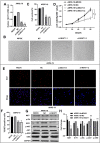
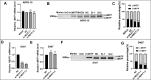
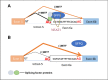
Results: NEAT1 was highly expressed in proliferative RPE cells, which had low expression of (-)MITF. Knockdown of NEAT1 in RPE cells switched the MITF splicing pattern to produce higher levels of (-)MITF and inhibited cell proliferation. Mechanistically, NEAT1 recruited SFPQ to bind directly with MITF mRNA to regulate its alternative splicing. Overexpression of SFPQ in ARPE-19 cells enhanced the binding enrichment of SFPQ to MITF and increased the splicing efficiency of (+)MITF. The binding affinity between SFPQ and MITF was decreased after NEAT1 knockdown.
Conclusions: NEAT1 acts as a scaffold to recruit SFPQ to MITF mRNA and promote its binding affinity, which plays an important role in regulating the alternative splicing of MITF and RPE cell proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zeb1 represses Mitf and regulates pigment synthesis, cell proliferation, and epithelial morphology.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Nov;50(11):5080-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2911. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19515996 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in the retinal pigment epithelium.Mol Vis. 2012;18:519-27. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Mol Vis. 2012. PMID: 22419845 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cell proliferation in the retinal pigment epithelium: Differential regulation of the death-associated protein like-1 DAPL1 by alternative MITF splice forms.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2018 May;31(3):411-422. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12676. Epub 2017 Dec 9. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2018. PMID: 29171181
-
A big gene linked to small eyes encodes multiple Mitf isoforms: many promoters make light work.Pigment Cell Res. 1998 Dec;11(6):329-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.1998.tb00491.x. Pigment Cell Res. 1998. PMID: 9870544 Review.
-
The transcription factor MITF in RPE function and dysfunction.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019 Nov;73:100766. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 23. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31242455 Review.
Cited by
-
Insight into the role of non-coding RNA in the diagnosis and treatment of retinitis pigmentosa.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Oct 29;9(1):44-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.10.011. eCollection 2024 Mar. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 38075200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress on Non-coding RNAs in Cholesteatoma of the Middle Ear.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 May;16(2):99-114. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2022.01319. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36560834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic roles and related mechanisms of the long non-coding RNA MINCR in human cancers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 5;11:1087337. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1087337. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37215074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoform balance of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 is regulated by the RNA-binding protein QKI, governs the glioma transcriptome, and impacts cell migration.J Biol Chem. 2024 Aug;300(8):107595. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107595. Epub 2024 Jul 18. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39032650 Free PMC article.
-
NEAT1 regulates BMSCs aging through disruption of FGF2 nuclear transport.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jan 29;16(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04156-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39876006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strauss O. The retinal pigment epithelium in visual function. Physiol Rev. 2005; 85: 845–881. - PubMed
-
- Rapaport DH, Rakic P, Yasamura D, LaVail MM.. Genesis of the retinal pigment epithelium in the macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1995; 363: 359–376. - PubMed
-
- Leiderman YI, Miller JW.. Proliferative vitreoretinopathy: pathobiology and therapeutic targets. Semin Ophthalmol. 2009; 24: 62–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

