Emodin Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome-Dependent Pyroptosis Signaling Pathway In vitro and In vivo
- PMID: 34787801
- PMCID: PMC8956541
- DOI: 10.1007/s10753-021-01581-1
Emodin Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome-Dependent Pyroptosis Signaling Pathway In vitro and In vivo
Abstract
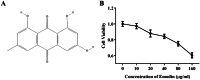
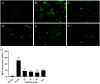
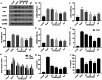
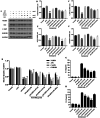
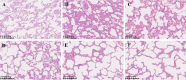
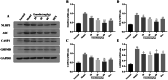
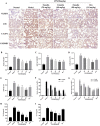
Emodin, the effective component of the traditional Chinese medicine Dahuang, has anti-inflammatory effects. However, the protective effects and potential mechanisms of emodin are not clear. This study investigated the protective effects and potential mechanisms of emodin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) in vitro and in vivo. In vivo, we designed an LPS-induced ALI rat model. In vitro, we chose the J774A.1 cell line to establish an inflammatory cellular model, and knocked down NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) using small interfering RNA. The mRNA and protein expression of NLRP3, a C-terminal caspase recruitment domain (ASC), caspase 1 (CASP1), and gasdermin D (GSDMD) in cells and lung tissues were detected by western blot and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The expression levels of interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) and IL-18 in the serum and supernatant were determined by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The degree of pathological injury in lung tissue was evaluated by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. In vitro, we demonstrated that emodin could inhibit NLRP3 and then inhibit the expression of ASC, CASP1, GSDMD, IL-1β, and IL-18. In vivo, we confirmed that emodin had protective effects on LPS-induced ALI and inhibitory effects on NLRP3 inflammasome -dependent pyroptosis. Emodin showed excellent protective effects against LPS-induced ALI by regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis signaling pathway.
Keywords: LPS; NLRP3 inflammasome; acute lung injury; emodin; pyroptosis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
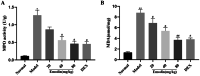
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

