Screening for mild cognitive impairment in people with obesity: a systematic review
- PMID: 34789218
- PMCID: PMC8600927
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-021-00898-0
Screening for mild cognitive impairment in people with obesity: a systematic review
Abstract
Objective: Recent evidence demonstrates that obesity is associated with developing cognitive impairment. However, evidence related to the assessment of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in people with obesity is limited. Therefore, this systematic review aimed to examine evidence concerning the screening of MCI in people with obesity from the general population.
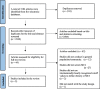
Method: We conducted a systematic search of CINHAL, EMBASE, MEDLINE, PsycINFO and PubMed electronic databases for observational studies to assess MCI in people with obesity from the general population. PRISMA guideline was followed. The articles published from January 2011 to July 2021 were included.
Results: Database search found 3104 sources. After the screening process, two articles from China and Egypt were included. The main age groups assessed were middle-aged adulthood and older adulthood. There were no studies undertaken in young adults or across the life span. Obesity was assessed by body mass index. MCI was assessed by cognitive screening tools; Mini-mental State Examination and Addenbrooke's Cognitive Examination. The prevalence of MCI in people with obesity was 18.5 % and 42.9 % in Chinese and Egyptian studies, respectively. Only one study supported a positive association between MCI and obesity.
Conclusions: Limited studies were found on screening MCI in people with obesity in the general population. The available evidence was not adequate to explain the overall prevalence, possible associations, and the best tool for assessing MCI in people with obesity. Expanding screening studies for MCI in people with obesity in the general population is essential.
Keywords: General population; Mild cognitive impairment; Obesity; Screening.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to be declared including the financial or personal relationship of any organisation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Prevalence of Mild Cognitive Impairment among Chinese People: A Meta-Analysis.Neuroepidemiology. 2021;55(2):79-91. doi: 10.1159/000512597. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Neuroepidemiology. 2021. PMID: 33756479
-
Validation of the Addenbrooke's Cognitive Examination-III in Mild Cognitive Impairment in Arabic Speakers in Egypt.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2020;49(4):418-422. doi: 10.1159/000510952. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2020. PMID: 33080612
-
Validity of screening tools for dementia and mild cognitive impairment among the elderly in primary health care: a systematic review.Public Health. 2019 Apr;169:84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30826688
-
Validation of the Mini-Addenbrooke's Cognitive Examination in Mild Cognitive Impairment in Arabic Speakers.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2021;50(2):178-182. doi: 10.1159/000517580. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2021. PMID: 34293741
-
Is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) test better suited than the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) detection among people aged over 60? Meta-analysis.Psychiatr Pol. 2016 Oct 31;50(5):1039-1052. doi: 10.12740/PP/45368. Psychiatr Pol. 2016. PMID: 27992895 Review. English, Polish.
Cited by
-
Primary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Cognitive Dysfunction in Young Adults: Results from a Cross-Sectional Controlled Study.Behav Sci (Basel). 2024 Apr 12;14(4):321. doi: 10.3390/bs14040321. Behav Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667117 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Obesity and Its Impact on Cognitive Impairments-A Narrative Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 10;12(5):1071. doi: 10.3390/antiox12051071. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Inflammatory Index and Cognitive Function: Findings from a Cross-Sectional Study in Obese Chinese Township Population from 45 to 75 Years.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Apr 18;17:2365-2382. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S447300. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38651005 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of intermittent fasting on preventing obesity-related early aging from a molecular and cellular perspective.J Med Life. 2024 Mar;17(3):261-272. doi: 10.25122/jml-2023-0370. J Med Life. 2024. PMID: 39044934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overlooked cases of mild cognitive impairment: Implications to early Alzheimer's disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Jul;98:102335. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102335. Epub 2024 May 12. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38744405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chooi YC, Ding C, Magkos F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism. 2019;92:6–10. - PubMed
-
- Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;138:271–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical