Association of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio with Efficacy of First-Line Avelumab plus Axitinib vs. Sunitinib in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma Enrolled in the Phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 Trial
- PMID: 34789480
- PMCID: PMC9377757
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1688
Association of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio with Efficacy of First-Line Avelumab plus Axitinib vs. Sunitinib in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma Enrolled in the Phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 Trial
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and efficacy of avelumab plus axitinib or sunitinib.
Experimental design: Adult patients with untreated advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with a clear-cell component, ≥1 measurable lesions, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1, fresh or archival tumor specimen, and adequate renal, cardiac, and hepatic function were included. Retrospective analyses of the association between baseline NLR and progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the avelumab plus axitinib or sunitinib arms were performed using the first interim analysis of the phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 trial (NCT02684006). Multivariate Cox regression analyses of PFS and OS were conducted. Translational data were assessed to elucidate the underlying biology associated with differences in NLR.
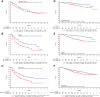
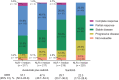
Results: Patients with below-median NLR had longer observed PFS with avelumab plus axitinib [stratified HR, 0.85; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.634-1.153] or sunitinib (HR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.415-0.745). In the avelumab plus axitinib or sunitinib arms, respectively, median PFS was 13.8 and 11.2 months in patients with below-median NLR, and 13.3 and 5.6 months in patients with median-or-higher NLR. Below-median NLR was also associated with longer observed OS in the avelumab plus axitinib (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.300-0.871) and sunitinib arms (HR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.174-0.511). Tumor analyses showed an association between NLR and key biological characteristics, suggesting a role of NLR in underlying mechanisms influencing clinical outcome.
Conclusions: Current data support NLR as a prognostic biomarker in patients with advanced RCC receiving avelumab plus axitinib or sunitinib.
©2021 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Comment in
- Clin Cancer Res. 28:569.
- Clin Cancer Res. 28:569.
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures. 2020. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2020. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts.... - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mahdavifar NMM, Ghoncheh M, Salehiniya H. Incidence, mortality and risk factors of kidney cancer in the world. WCRJ 2018;5:1–9.
-
- Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Šeruga B, Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocana A, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 2014;106:dju124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

