Giant Esophageal Leiomyoma: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges
- PMID: 34789714
- PMCID: PMC8609978
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.934557
Giant Esophageal Leiomyoma: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges
Abstract
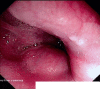
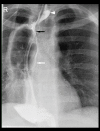
BACKGROUND Leiomyoma is a rare, benign, esophageal tumor that does not often measure >10 cm. Here, we report a case of giant esophageal leiomyoma in a 24-year-old man. CASE REPORT A 24-year-old man who smoked and had primary hypertension and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency presented with a history of shortness of breath and productive cough with yellowish sputum, a long history of dysphagia to solid food, and a weight loss of 7 kg over 2 months. A chest X-ray revealed a mediastinum with a width >8 cm. Computed tomography of the patient's chest revealed a multilobulated mass that originated from the upper and middle thoracic esophagus, caused severe narrowing of his esophageal lumen, and was compressing his trachea and right main bronchus. Resection of the tumor was performed and, because of the large defect after the surgery and the mucosal necrosis, the patient underwent an Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy. His postoperative course was uneventful. He had no symptoms when he was seen in the outpatient clinic for follow-up and fully recovered. CONCLUSIONS Giant esophageal leiomyoma (GEL) is a rare oncological entity that presents several diagnostic and therapeutic challenges because of the scarcity of information in the medical literature on surgical management. The descriptions of techniques for surgical resection of GEL do not include ways to effectively perform subsequent reconstruction. The aim of the present paper was to contribute to this scant information by reporting our experience with performing an Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy to manage a case of GEL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Enucleation for a giant esophageal leiomyoma; report of a case].Kyobu Geka. 2004 Dec;57(13):1245-9. Kyobu Geka. 2004. PMID: 15609667 Japanese.
-
A Giant Upper Esophageal Leiomyoma: A Rare Case.Am J Case Rep. 2021 Oct 15;22:e932430. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.932430. Am J Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34653118 Free PMC article.
-
Esophageal resection for giant leiomyoma: report of two cases and a review of the literature.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2009 Jul;394(4):623-9. doi: 10.1007/s00423-008-0365-8. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2009. PMID: 18594855
-
Thoracoscopic resection of a giant leiomyoma of the esophagus with a mediastinal outgrowth.Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998 Dec;4(6):351-3. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998. PMID: 9914465 Review.
-
[Thoracotomy enucleation of a giant leiomyoma of the upper oesophagus. Case report and review of the literature].Chir Ital. 2007 Jan-Feb;59(1):123-9. Chir Ital. 2007. PMID: 17361941 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Slicing Through the Options: A Systematic Review of Esophageal Leiomyoma Management.Cureus. 2025 Apr 2;17(4):e81614. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81614. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40177232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Rare Case of Giant Esophageal Leiomyoma in an Adult Male Presenting With Right Upper Quadrant Pain and Mild Dysphagia.Cureus. 2025 Aug 4;17(8):e89349. doi: 10.7759/cureus.89349. eCollection 2025 Aug. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40909068 Free PMC article.
-
To Be, or Not to Be … Pectoral Angina? The Pain Is the Same, but the Etiology Is Different-A Case Report.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 26;14(9):1066. doi: 10.3390/life14091066. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337851 Free PMC article.
-
A Large Esophageal Leiomyoma: Thoraco-Laparoscopic Enucleation or Esophagectomy and Reconstruction?Am J Case Rep. 2023 Dec 22;24:e942371. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.942371. Am J Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 38134004 Free PMC article.
-
Leiomyoma of the esophagus: A case report and review of the literature.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022 May;94:107078. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2022.107078. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35439728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seremetis MG, Lyons WS, Deguzman VC, Peabody JW. Leiomyomata of the esophagus. An analysis of 838 cases. Cancer. 1976;38(5):2166–77. - PubMed
-
- Lee LS, Singhal S, Brinster CJ, et al. Current management of esophageal leiomyoma. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198(1):136–46. - PubMed
-
- Gupta V, Sinha SK, Vaiphei K, Lal A. Esophageal resection for giant leiomyoma. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015;11(3):651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

