Cold and heterogeneous T cell repertoire is associated with copy number aberrations and loss of immune genes in small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 34789716
- PMCID: PMC8599854
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-26821-8
Cold and heterogeneous T cell repertoire is associated with copy number aberrations and loss of immune genes in small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
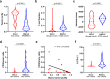
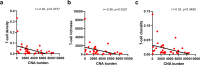
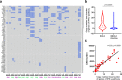
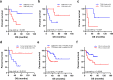
Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) is speculated to harbor complex genomic intratumor heterogeneity (ITH) associated with high recurrence rate and suboptimal response to immunotherapy. Here, using multi-region whole exome/T cell receptor (TCR) sequencing as well as immunohistochemistry, we reveal a rather homogeneous mutational landscape but extremely cold and heterogeneous TCR repertoire in limited-stage SCLC tumors (LS-SCLCs). Compared to localized non-small cell lung cancers, LS-SCLCs have similar predicted neoantigen burden and genomic ITH, but significantly colder and more heterogeneous TCR repertoire associated with higher chromosomal copy number aberration (CNA) burden. Furthermore, copy number loss of IFN-γ pathway genes is frequently observed and positively correlates with CNA burden. Higher mutational burden, higher T cell infiltration and positive PD-L1 expression are associated with longer overall survival (OS), while higher CNA burden is associated with shorter OS in patients with LS-SCLC.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
L.A.B. serves on advisory committees for AstraZeneca, AbbVie, GenMab, BergenBio, Pharma Mar SA, Sierra Oncology, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, and Pfizer, and has research support from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, GenMab, Sierra Oncology, and Tolero Pharmaceuticals. I.W. reports grants and personal fees from Genentech/Roche, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca/Medimmune, Pfizer, HTG Molecular, Merck, and Guardant Health; personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline and MSD; grants from Oncoplex, DepArray, Adaptive, Adaptimmune, EMD Serono, Takeda, Amgen, Karus, Johnson & Johnson, Iovance, 4D, Novartis, Oncocyte, and Akoya. J.Z. reports research funding from Merck, Johnson and Johnson, and consultant fees from BMS, Johnson and Johnson, AstraZeneca, Geneplus, OrigMed, and Innovent outside the submitted work. J.V.H. reports honorariums from AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Catalyst, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Guardant Health, Foundation medicine, Hengrui Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Spectrum, EMD Serono, Sanofi, Takeda, Mirati Therapeutics, BMS, BrightPath Biotherapeutics, Janssen Global Services, Nexus Health Systems, EMD Serono, Pneuma Respiratory, Kairos Venture Investments, Roche, and Leads Biolabs. A.R. serves on the Scientific Advisory Board and has received honoraria from Adaptive Biotechnologies. X.L. receives consulting/advisory fees from EMD Serono (Merck KGaA), AstraZeneca, Spectrum Pharmaceutics, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Hengrui Therapeutics, and AbbVie, and research funding to the institute from Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim. R.K.T. is a founder of NEO New Oncology, acquired by Siemens Healthcare, a founder of PearlRiver Bio, acquired by Centessa, a founder of Epiphanes Inc. and a shareholder of Centessa and Epiphanes. R.K.T. has received honoraria from PearlRiver Bio. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Howlader, N. et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2016 (National Cancer Institute, 2019).
-
- Govindan R, et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:4539–4544. - PubMed
-
- Micke P, et al. Staging small cell lung cancer: Veterans Administration Lung Study Group versus International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer—what limits limited disease? Lung Cancer. 2002;37:271–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

