Reverse-translational identification of a cerebellar satiation network
- PMID: 34789878
- PMCID: PMC8665128
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04143-5
Reverse-translational identification of a cerebellar satiation network
Abstract
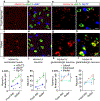
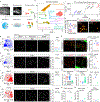
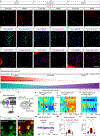
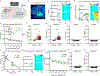
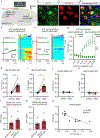
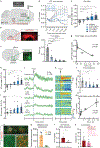
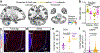
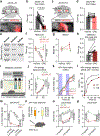
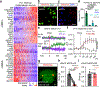
The brain is the seat of body weight homeostasis. However, our inability to control the increasing prevalence of obesity highlights a need to look beyond canonical feeding pathways to broaden our understanding of body weight control1-3. Here we used a reverse-translational approach to identify and anatomically, molecularly and functionally characterize a neural ensemble that promotes satiation. Unbiased, task-based functional magnetic resonance imaging revealed marked differences in cerebellar responses to food in people with a genetic disorder characterized by insatiable appetite. Transcriptomic analyses in mice revealed molecularly and topographically -distinct neurons in the anterior deep cerebellar nuclei (aDCN) that are activated by feeding or nutrient infusion in the gut. Selective activation of aDCN neurons substantially decreased food intake by reducing meal size without compensatory changes to metabolic rate. We found that aDCN activity terminates food intake by increasing striatal dopamine levels and attenuating the phasic dopamine response to subsequent food consumption. Our study defines a conserved satiation centre that may represent a novel therapeutic target for the management of excessive eating, and underscores the utility of a 'bedside-to-bench' approach for the identification of neural circuits that influence behaviour.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures
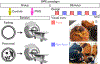
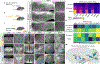
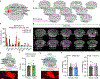

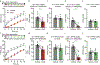
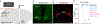


Comment in
-
Cerebellar neurons that curb food consumption.Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7888):229-230. doi: 10.1038/d41586-021-03383-9. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34789886 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK104772/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 NS105555/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114104/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 857082/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- R00 DK119574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116170/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK131558/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 MH125995/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01 DK124801/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01 DK114104/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U19 NS112959/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS111479/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK124801/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 17SDG33400158/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- R01 MH111868/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

