Audit of requests for disability certification of adults received at a tertiary care general hospital psychiatry unit
- PMID: 34789938
- PMCID: PMC8522620
- DOI: 10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_1188_20
Audit of requests for disability certification of adults received at a tertiary care general hospital psychiatry unit
Abstract
Background: Persons with disability (PwD) are entitled to certain benefits from the State on grounds of being disabled. With the recent enactment of the Rights of PwD Act, 2016, and increased efforts to provide assistance to persons with certifiable disabilities, data pertaining to disability requests can be useful to understand the way in which services are utilized.
Materials and methods: This study is an audit of the disability certificates issued to all subjects with age ≥18 years between 2016 and 2019 at a tertiary care general hospital psychiatry unit, and discusses the pattern and profile of the certificates.
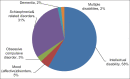
Results: A total of 356 patients were issued disability certificates (2016-2019). The mean age of the subjects was 32.8 (±11.2) years and about 30% of them were females. Intellectual disability (58.3%) was the most common diagnosis, followed by schizophrenia and related disorders (31%), while all other disorders constituted a smaller proportion (11%) of the sample. About 60% of the subjects had moderate disability, 37.4% had severe disability, and 1.7% had profound disability.
Conclusion: A large majority of the certificates were issued to subjects with intellectual disability. Patients with severe mental illnesses are probably not accessing the disability benefits optimally. This audit also points to under-representation of women as well as an overall underutilization of services by individuals with mental disability.
Keywords: Certificates; India; disability; mental disorders.
Copyright: © 2021 Indian Journal of Psychiatry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sociodemographic and clinical profile of patients receiving disability certificates for psychiatric disorders: An Indian Psychiatric Society Multicentric study.Indian J Psychiatry. 2022 Jul-Aug;64(4):335-341. doi: 10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_236_22. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Indian J Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36060714 Free PMC article.
-
Five-Year Trend in Issuing Disability Certificates from a General Hospital Psychiatric Unit in South India.Indian J Psychol Med. 2020 Aug 25;42(5):451-455. doi: 10.1177/0253717620947163. eCollection 2020 Sep. Indian J Psychol Med. 2020. PMID: 33414592 Free PMC article.
-
Disability certificates in India: a challenge to health privacy.Indian J Med Ethics. 2012 Jan-Mar;9(1):43-5. doi: 10.20529/IJME.2012.010. Indian J Med Ethics. 2012. PMID: 22319852 Free PMC article.
-
The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act 2016: Mental Health Implications.Indian J Psychol Med. 2019 Mar-Apr;41(2):119-125. doi: 10.4103/IJPSYM.IJPSYM_364_18. Indian J Psychol Med. 2019. PMID: 30983658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[What Psychiatrists Should Know about the Medical Documentation They Issue: Admission for Medical Care and Protection, Medical Treatment for Persons with Disabilities, Mental Health Disability Certification, etc].Seishin Shinkeigaku Zasshi. 2015;117(7):550-5. Seishin Shinkeigaku Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 26552320 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Sociodemographic and clinical profile of patients receiving disability certificates for psychiatric disorders: An Indian Psychiatric Society Multicentric study.Indian J Psychiatry. 2022 Jul-Aug;64(4):335-341. doi: 10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_236_22. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Indian J Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36060714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 (GBD 2010) Disability Weights. Seattle, USA: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME); 2012.
-
- UN World Health Organization (WHO). World Report on Disability: Summary. WHO/NMH/VIP/11.01. 2011. [Last accessed on 2020 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.refworld.org/docid/50854a322.html .
-
- Disabled Persons in India: A Statistical Profile 2016. Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, Government of India. [Last accessed on 2020 Sep 27]. Available from: https://ruralindiaonline.org/library/resource/disabled-persons-in-india-...
-
- Census of India. The Office of the Registrar and Census Commissioner, India, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. 2011. [Last accessed on 2021 Jun 11]. Available from: http://www.censusindia.gov.in/
-
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016. Ministry of Law and Justice, the Gazzette of India. 2016. [Last accessed on 2021 Jun 11]. Available from: http://www.disabilityaffairs.gov.in/uploaad/uploadfiles/files/RPWD/ACT/2... .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources