An Unusual Case of Acute Dyspnoea: Acute Intrathoracic Gastric Volvulus with Probable Tension Gastrothorax
- PMID: 34790622
- PMCID: PMC8592663
- DOI: 10.12890/2021_002818
An Unusual Case of Acute Dyspnoea: Acute Intrathoracic Gastric Volvulus with Probable Tension Gastrothorax
Abstract
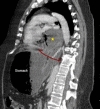
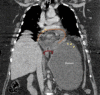
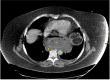
Acute gastric volvulus is a rare complication affecting 4% of hiatal hernias. It is described as an abnormal rotation of the stomach around a transverse or longitudinal axis and can be intra-abdominal or intrathoracic. Intrathoracic gastric volvulus can lead to tension gastrothorax, which is defined as the presence of a massive gastric distension in the chest cavity causing a mediastinal shift with haemodynamic instability and a risk of cardiorespiratory arrest. We report a case of intrathoracic gastric volvulus with probable tension gastrothorax. Early diagnosis of gastrothorax with computed tomography and immediate insertion of a nasogastric tube resulted in rapid clinical improvement. Surgical intervention is the treatment of choice.
Learning points: Tension gastrothorax should be suspected in the presence of abdominal and chest pain, vomiting and haemodynamic instability.Prompt diagnosis and treatment are necessary to reduce morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: Volvulus gastric; gastrothorax; hiatal hernia.
© EFIM 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hillemand P, Bernard HJ, Villard J. À propos des volvulus gastriques. Sem Hop Paris. 1955;31:2890–2899. - PubMed
-
- Marini L, Azarian R, Gagadoux F, Brion N, Petitpretz P. Gastric volvulus associated with Zenker’s diverticulum: a rare cause of recurrent pneumopathy. Rev Mal Respir. 2000;17:121–123. - PubMed
-
- Rashid A, Thangarajah T, Mulvey D, Larvin M, Iftikhar AY. A review article on gastric volvulus: a challenge to diagnosis and management. Int J Surg. 2010;8:18–24. - PubMed
-
- Horst M, Sacher P, Molz G, Willi UV, Meuli M. Tension gastrothorax. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40:1500–1504. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
