The Role of HLA Antigens and Steroid Dose on the Course of COVID-19 of Patients After Kidney Transplantation
- PMID: 34790673
- PMCID: PMC8591240
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.730156
The Role of HLA Antigens and Steroid Dose on the Course of COVID-19 of Patients After Kidney Transplantation
Abstract
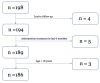
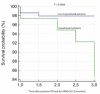
Background: Kidney transplant recipients appear to be at higher risk for critical COVID-19. Our analysis aimed to identify the possible risk factors for a severe course of the COVID-19 disease and to determine the influence of selected human leukocyte antigens (HLAs) on the course of the disease. Methods: This is a retrospective, multicenter analysis that included patients that were confirmed to be severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) positive after kidney transplantation (KT). The group of patients was divided into two subgroups according to the course of the infection, as follows: non-hospitalized and hospitalized. Results: A total of 186 patients (men, 69.4%) with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 positivity were included in the group. The following independent risk factors for the outcome of hospitalization were identified: the age at the time of infection [odds ratio (OR) = 1.19, P < 0.0001], a body mass index (BMI) >29.9 kg/m2 (OR = 7.21, P < 0.0001), <7.5-mg prednisone dose/day (OR = 2.29, P = 0.0008), and HLA-DQ2 with a protective nature (OR = 0.05, P = 0.0034). Conclusions: Higher doses of corticosteroids (>7.5 mg/kg) in standard immunosuppressive regimes and HLA-DQ2 appear to be protective factors in our analysis.
Keywords: COVID-19; HLA class I and class II typing; immunosuppression; kidney transplantation; steroid dose.
Copyright © 2021 Dedinská, Skálová, Graňák, Vnučák, Baltesová, Žilinská and Jeseňák.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous