Lichen Planus
- PMID: 34790675
- PMCID: PMC8591129
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.737813
Lichen Planus
Abstract
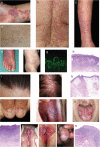
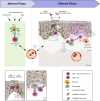
Lichen planus (LP) is a T cell-mediated disease affecting the stratified squamous epithelia of the skin and/or mucus membrane. Histologically, the disease is characterized by a lichenoid inflammatory infiltrate and vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer of the epidermis. LP has three major subtypes: Cutaneous, mucosal and appendageal LP. Rarely, it may affect the nails in the absence of skin and/or mucosal changes. LP may also be induced by several drugs, typically anti-hypertensive medication or be associated with infections, particularly viral hepatitis. The diagnosis is based on the clinical presentation and characteristic histological findings. Although the disease is often self-limiting, the intractable pruritus and painful mucosal erosions result in significant morbidity. The current first-line treatment are topical and/or systemic corticosteroids. In addition, immunosuppressants may be used as corticosteroid-sparing agents. These, however are often not sufficient to control disease. Janus kinase inhibitors and biologics (anti-IL-12/23, anti-IL17) have emerged as novel future treatment options. Thus, one may expect a dramatic change of the treatment landscape of LP in the near future.
Keywords: T-cell mediated; inflammation; lichen planus; skin disease; treatment.
Copyright © 2021 Boch, Langan, Kridin, Zillikens, Ludwig and Bieber.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shiohara T, Moriya N, Mochizuki T, Nagashima M. Lichenoid tissue reaction (LTR) induced by local transfer of Ia-reactive T-cell clones. II LTR by epidermal invasion of cytotoxic lymphokine-producing autoreactive T cells. J Investig Dermatol. (1987) 89:8–14. 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12523539 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yasukawa M, Ohminami H, Arai J, Kasahara Y, Ishida Y, Fujita S. Granule exocytosis, and not the fas/fas ligand system, is the main pathway of cytotoxicity mediated by alloantigen-specific CD4(+) as well as CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes in humans. Blood. (2000) 95:2352–5. 10.1182/blood.V95.7.2352 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

