Magnetic resonance quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion in hepatic fibrosis staging: a pilot study of diffusion kurtosis imaging to identify reversible hepatic fibrosis
- PMID: 34790775
- PMCID: PMC8576693
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-4884
Magnetic resonance quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion in hepatic fibrosis staging: a pilot study of diffusion kurtosis imaging to identify reversible hepatic fibrosis
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) in differentiating early hepatic fibrosis (HF) from normal liver and advanced HF in rabbits.
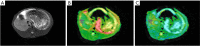
Methods: A total of 35 healthy New Zealand white rabbits were included in the study. A model of HF was established in 30 rabbits through subcutaneous injections of 50% carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)/olive oil, while 5 rabbits received saline injections. The gradually increased doses of CCl4 were 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3 mL/kg in weeks 1 to 3, weeks 4 to 6, and weeks 7 to 10, respectively. Two injections were given each week. Two rabbits in the experimental group died. All rabbits underwent DKI with three b values (0, 500, and 1,000 s/mm2) at week 5 (n=8), week 6 (n=9), week 7 (n=8), and week 10 (n=8). Approximately 2 liver lobes per rabbit were selected for histopathology. Mean diffusivity (MD) and mean kurtosis (MK) were calculated. Discrimination capacities of DKI parameters were analyzed and compared by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis.
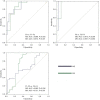
Results: The meta-analysis of histological data in viral hepatitis (METAVIR) scoring system was used to classify liver lobes into the control group (F0, n=0), early HF group (F1-F2, n=28), and advanced HF group (F3-F4, n=28). MD and MK values were significantly different among the three groups (all P<0.05). MD value was negatively correlated with increased fibrosis level, while MK value was positively correlated with increased fibrosis level (ρ=-0.540, 0.614; P<0.05). The area under ROC curves (AUCs) for MD and MK were 0.886 and 0.875, respectively, for characterization of F0 and F1-F2, and 0.975 and 0.957 for F0 and F3-F4. AUC for MK was 0.751 for characterization of F1-F2 and F3-F4. MD performed better than MK for characterization of F0 and F1-F2 as well as F0 and F3-F4. MK showed good differentiation performance between F1-F2 and F3-F4.
Conclusions: Our results showed that DKI contributed to discriminating reversible early HF from normal liver and advanced HF and as a result, showed promise for use in HF diagnosis.
Keywords: Hepatic fibrosis (HF); diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI); magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); staging diagnosis.
2021 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-4884). All authors reported that this study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, China (No. 201602228). The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
