Synergistic effect of chidamide and venetoclax on apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells and its mechanism
- PMID: 34790781
- PMCID: PMC8576699
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-5066
Synergistic effect of chidamide and venetoclax on apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells and its mechanism
Abstract
Background: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a hematological malignancy with a low remission rate and high recurrence rate. Overexpression of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 is associated with a lower overall survival rate in AML patients. Venetoclax (ABT199) is a selective inhibitor of Bcl-2 that has a significant effect in AML, but single-drug resistance often occurs due to the high expression of Mcl-1 protein. Studies have confirmed that chidamide can downregulate the expression levels of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 and induce apoptosis.
Methods: This study aimed to use AML cell lines and primary cells to study the effects of venetoclax and chidamide combination therapy on AML cell apoptosis, the cell cycle, and changes in related signaling pathways in vitro; establish an AML mouse model to observe the efficacy and survival time of combination therapy in vivo; and analyze the drug effects with multi-omics sequencing technology. The changes in gene and protein expression before and after treatment were examined to clarify the molecular mechanism driving the synergistic effect of the two drugs.
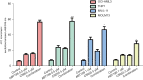
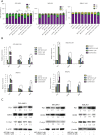
Results: (I) Both venetoclax and chidamide promoted apoptosis in AML cell lines and primary cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. The effect was further enhanced when the two drugs were combined, and a synergistic effect was observed (combination index <1). (II) At both the mRNA and protein levels, the expression of Mcl-1 was upregulated by venetoclax and downregulated by chidamide, and the expression of Mcl-1 decreased further after combination treatment. (III) Transcriptome sequencing showed that differentially expressed genes in the combination group compared with the venetoclax monotherapy group were mainly enriched in the PI3K-AKT pathway and JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Moreover, qRT-PCR and Western blot confirmed these results. (IV) The combination therapy group exhibited significantly inhibited disease progression and a prolonged survival time among AML mice.
Conclusions: Chidamide combined with venetoclax synergistically promoted apoptosis in AML cell lines and primary cells by inhibiting activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway and JAK2/STAT3 pathway.
Keywords: Chidamide; acute myeloid leukemia (AML); apoptosis; mechanism; venetoclax.
2021 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-5066). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Oridonin Synergistically Enhances the Pro-Apoptotic Effect of Venetoclax on Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells by Inhibiting AKT Signaling.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Sep 6;28(9):195. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2809195. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37796705
-
Synergistic efficacy of homoharringtonine and venetoclax on acute myeloid leukemia cells and the underlying mechanisms.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Apr;10(8):490. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-1459. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35571387 Free PMC article.
-
Superior anti-tumor activity of the MDM2 antagonist idasanutlin and the Bcl-2 inhibitor venetoclax in p53 wild-type acute myeloid leukemia models.J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Jun 28;9(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0280-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27353420 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted therapy with a selective BCL-2 inhibitor in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia.Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2019 Apr-Jun;41(2):169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.htct.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Dec 29. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2019. PMID: 31084767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Venetoclax in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2023;18(1):11-28. doi: 10.2174/1574892817666220429105338. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2023. PMID: 35507786 Review.
Cited by
-
Current treatment strategies targeting histone deacetylase inhibitors in acute lymphocytic leukemia: a systematic review.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 21;14:1324859. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1324859. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38450195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine Cytotoxin Santacruzamate A Derivatives as Potent HDAC1-3 Inhibitors and Their Synergistic Anti-Leukemia Effects with Venetoclax.Mar Drugs. 2024 May 28;22(6):250. doi: 10.3390/md22060250. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38921561 Free PMC article.
-
Apicidin confers promising therapeutic effect on acute myeloid leukemia cells via increasing QPCT expression.Cancer Biol Ther. 2023 Dec 31;24(1):2228497. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2023.2228497. Cancer Biol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37381175 Free PMC article.
-
Chidamide suppresses adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells via increasing REEP2 expression.iScience. 2023 Feb 16;26(3):106221. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106221. eCollection 2023 Mar 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36879811 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of BCL-2 and PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway in Pathogenesis of Myelodysplastic Syndromes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 1;24(5):4708. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054708. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Konopleva M, Pollyea DA, Potluri J, et al. Efficacy and Biological Correlates of Response in a Phase II Study of Venetoclax Monotherapy in Patients with Acute Myelogenous Leukemia. Cancer Discov 2016;6:1106-17. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0313 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
