Epione application: An integrated web‑toolkit of clinical genomics and personalized medicine in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 34791504
- PMCID: PMC8612305
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5063
Epione application: An integrated web‑toolkit of clinical genomics and personalized medicine in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
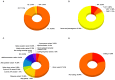
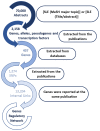
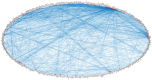
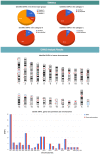
Genome wide association studies (GWAS) have identified autoimmune disease‑associated loci, a number of which are involved in numerous disease‑associated pathways. However, much of the underlying genetic and pathophysiological mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, highly heterogeneous autoimmune disease, characterized by differences in autoantibody profile, serum cytokines and a multi‑system involvement. This study presents the Epione application, an integrated bioinformatics web‑toolkit, designed to assist medical experts and researchers in more accurately diagnosing SLE. The application aims to identify the most credible gene variants and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with SLE susceptibility, by using patient's genomic data to aid the medical expert in SLE diagnosis. The application contains useful knowledge of >70,000 SLE‑related publications that have been analyzed, using data mining and semantic techniques, towards extracting the SLE‑related genes and the corresponding SNPs. Probable genes associated with the patient's genomic profile are visualized with several graphs, including chromosome ideograms, statistic bars and regulatory networks through data mining studies with relative publications, to obtain a representative number of the most credible candidate genes and biological pathways associated with the SLE. Furthermore, an evaluation study was performed on a patient diagnosed with SLE and is presented herein. Epione has also been expanded in family‑related candidate patients to evaluate its predictive power. All the recognized gene variants that were previously considered to be associated with SLE were accurately identified in the output profile of the patient, and by comparing the results, novel findings have emerged. The Epione application may assist and facilitate in early stage diagnosis by using the patients' genomic profile to compare against the list of the most predictable candidate gene variants related to SLE. Its diagnosis‑oriented output presents the user with a structured set of results on variant association, position in genome and links to specific bibliography and gene network associations. The overall aim of the present study was to provide a reliable tool for the most effective study of SLE. This novel and accessible webserver tool of SLE is available at http://geneticslab.aua.gr/epione/.
Keywords: bioinformatics; clinical informatics; data mining; genomics; systemic lupus erythematosus; variant analysis; whole exome sequencing; whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
DAS is the Editor-in-Chief for the journal, but had no personal involvement in the reviewing process, or any influence in terms of adjudicating on the final decision, for this article. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Ramos PS, Criswell LA, Moser KL, Comeau ME, Williams AH, Pajewski NM, Chung SA, Graham RR, Zidovetzki R, Kelly JA, et al. International Consortium on the Genetics of Systemic Erythematosus: A comprehensive analysis of shared loci between systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and sixteen autoimmune diseases reveals limited genetic overlap. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002406. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002406. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

