Reconstitution and use of highly active human CDK1:Cyclin-B:CKS1 complexes
- PMID: 34791727
- PMCID: PMC8819839
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.4233
Reconstitution and use of highly active human CDK1:Cyclin-B:CKS1 complexes
Abstract
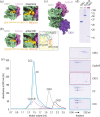
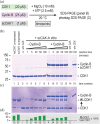
As dividing cells transition into mitosis, hundreds of proteins are phosphorylated by a complex of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) and Cyclin-B, often at multiple sites. CDK1:Cyclin-B phosphorylation patterns alter conformations, interaction partners, and enzymatic activities of target proteins and need to be recapitulated in vitro for the structural and functional characterization of the mitotic protein machinery. This requires a pure and active recombinant kinase complex. The kinase activity of CDK1 critically depends on the phosphorylation of a Threonine residue in its activation loop by a CDK1-activating kinase (CAK). We developed protocols to activate CDK1:Cyclin-B either in vitro with purified CAKs or in insect cells through CDK-CAK co-expression. To boost kinase processivity, we reconstituted a ternary complex consisting of CDK1, Cyclin-B, and CKS1. In this work, we provide and compare detailed protocols to obtain and use highly active CDK1:Cyclin-B (CC) and CDK1:Cyclin-B:CKS1 (CCC).
Keywords: CDK1; CKS1; cell cycle; cyclin; cyclin dependent kinase; cyclin-B; phosphorylation; phostag; processivity; recombinant protein.
© 2021 The Authors. Protein Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Protein Society.
Figures


References
-
- Morgan DO. The cell cycle: Principles of control. London, UK: New Science Press, 2007.
-
- Hochegger H, Takeda S, Hunt T. Cyclin‐dependent kinases and cell‐cycle transitions: Does one fit all? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:910–916. - PubMed
-
- Daub H, Olsen JV, Bairlein M, et al. Kinase‐selective enrichment enables quantitative phosphoproteomics of the kinome across the cell cycle. Mol Cell. 2008;31:438–448. - PubMed
-
- Olsen JV, Vermeulen M, Santamaria A, et al. Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveals widespread full phosphorylation site occupancy during mitosis. Sci Signal. 2010;3(ra3):ra3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

