Impact of docetaxel plus ramucirumab in a second-line setting after chemoimmunotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A retrospective study
- PMID: 34791812
- PMCID: PMC8758423
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.14236
Impact of docetaxel plus ramucirumab in a second-line setting after chemoimmunotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Chemoimmunotherapy has become a standard treatment option for patients with untreated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, numerous patients with advanced NSCLC develop disease progression. Therefore, the selection of second-line treatment after chemoimmunotherapy is crucial for improving clinical outcomes.
Methods: Of 88 enrolled patients with advanced NSCLC who received chemoimmunotherapy, we retrospectively evaluated 33 who received second-line chemotherapy after progression of chemoimmunotherapy at six centers in Japan. Among them, 18 patients received docetaxel plus ramucirumab and 15 patients received single-agent chemotherapy.
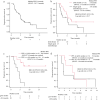
Results: The objective response rate in patients treated with docetaxel plus ramucirumab was significantly higher than that in patients treated with a single-agent chemotherapy regimen (55.6% vs. 0%, p < 0.001). The median progression-free survival (PFS) of patients who received docetaxel plus ramucirumab and single-agent chemotherapy was 5.8 months and 5.0 months, respectively (log-rank test p = 0.17). In the docetaxel plus ramucirumab regimen group, patients who responded to chemoimmunotherapy for ≥8.8 months had a significantly longer response to docetaxel plus ramucirumab than those who responded for <8.8 months (not reached vs. 4.1 months, log-rank test p = 0.003). In contrast, in the single-agent chemotherapy group, there was no significant difference in PFS between the ≥8.8- and <8.8-month PFS groups with chemoimmunotherapy (5.0 vs. 1.6 months, log-rank test p = 0.66).
Conclusion: Our retrospective observations suggest that the group with longer PFS with chemoimmunotherapy might be expected to benefit from docetaxel plus ramucirumab treatment in second-line settings for patients with advanced NSCLC.
Keywords: chemoimmunotherapy; docetaxel plus ramucirumab; non-small-cell lung cancer; performance status.
© 2021 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
T.Y. received grants from Pfizer, Ono Pharmaceutical, Chugai Pharmaceutical, and Takeda Pharmaceutical. K.T. received grants from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical, and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical, MSD, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Daiichi Sankyo. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prospective Observational Study of Ramucirumab Plus Docetaxel After Combined Chemoimmunotherapy in Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Oncologist. 2024 May 3;29(5):e681-e689. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyae001. Oncologist. 2024. PMID: 38241181 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Pembrolizumab Plus Docetaxel vs Docetaxel Alone in Patients With Previously Treated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The PROLUNG Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jun 1;6(6):856-864. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.0409. JAMA Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32271354 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of baseline symptom burden with efficacy outcomes: Exploratory analysis from the randomized phase III REVEL study in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2019 May;131:6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 2. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31027699 Clinical Trial.
-
The Role of the Antiangiogenetic Ramucirumab in the Treatment of Advanced Non Small Cell Lung Cancer.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(1):3-13. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666161118125103. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27855622 Review.
-
Clinical outcomes of ramucirumab plus docetaxel in the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer after immunotherapy: a systematic literature review.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 4;13:1247879. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1247879. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37731641 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Safety of Docetaxel plus Ramucirumab for Patients with Pretreated Advanced or Recurrent Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Focus on Older Patients.Target Oncol. 2024 May;19(3):411-421. doi: 10.1007/s11523-024-01045-0. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Target Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38467958
-
Efficacy of second- and third-line chemotherapy after chemotherapy with platinum doublet and immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: a descriptive study.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 30;14(7):4348-4356. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2024-2555. Epub 2025 Jul 22. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40792163 Free PMC article.
-
Docetaxel Plus Ramucirumab With Primary Prophylactic Pegylated Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor Support for Elderly Patients With Advanced NSCLC: A Multicenter Prospective Single Arm Phase 2 Trial: DRAGON Study (WJOG9416L).JTO Clin Res Rep. 2023 Aug 23;4(10):100569. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2023.100569. eCollection 2023 Oct. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2023. PMID: 37822699 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Previous Therapy for Neutropenia Caused by Combination Therapy of Ramucirumab and Docetaxel.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 30;16(11):2076. doi: 10.3390/cancers16112076. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893195 Free PMC article.
-
Treatments and Outcomes After Platinum-Based Chemotherapy and Anti-PD-(L)1 in NSCLC.JAMA Netw Open. 2025 Jun 2;8(6):e2514527. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.14527. JAMA Netw Open. 2025. PMID: 40526385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Ortiz AP, Fedewa SA, Pinheiro PS, Tortolero‐Luna G, et al. Cancer statistics for Hispanics/Latinos, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):425–45. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi L, Rodríguez‐Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, de Angelis F, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(22):2078–92. - PubMed
-
- Paz‐Ares L, Luft A, Vicente D, Tafreshi A, Gümüş M, Mazières J, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for squamous non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(21):2040–51. - PubMed
-
- Socinski MA, Jotte RM, Cappuzzo F, Orlandi F, Stroyakovskiy D, Nogami N, et al. Atezolizumab for first‐line treatment of metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(24):2288–301. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

