Prediction of cytochromes P450 3A and 2C19 modulation by both inflammation and drug interactions using physiologically based pharmacokinetics
- PMID: 34791831
- PMCID: PMC8752107
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.12730
Prediction of cytochromes P450 3A and 2C19 modulation by both inflammation and drug interactions using physiologically based pharmacokinetics
Abstract
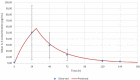
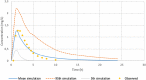
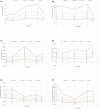
Xenobiotics can interact with cytochromes P450 (CYPs), resulting in drug-drug interactions, but CYPs can also contribute to drug-disease interactions, especially in the case of inflammation, which downregulates CYP activities through pretranscriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms. Interleukin-6 (IL-6), a key proinflammatory cytokine, is mainly responsible for this effect. The aim of our study was to develop a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model to foresee the impact of elevated IL-6 levels in combination with drug interactions with esomeprazole on CYP3A and CYP2C19. Data from a cohort of elective hip surgery patients whose CYP3A and CYP2C19 activities were measured before and after surgery were used to validate the accurate prediction of the developed models. Successive steps were to fit models for IL-6, esomeprazole, and omeprazole and its metabolite from the literature and to validate them. The models for midazolam and its metabolite were obtained from the literature. When appropriate, a correction factor was applied to convert drug concentrations from whole blood to plasma. Mean ratios between simulated and observed areas under the curve for omeprazole/5-hydroxy omeprazole, esomeprazole, and IL-6 were 1.53, 1.06, and 0.69, respectively, indicating an accurate prediction of the developed models. The impact of IL-6 and esomeprazole on the exposure to CYP3A and CYP2C19 probe substrates and respective metabolites were correctly predicted. Indeed, the ratio between predicted and observed mean concentrations were <2 for all observations (ranging from 0.51 to 1.7). The impact of IL-6 and esomeprazole on CYP3A and CYP2C19 activities after a hip surgery were correctly predicted with the developed PBPK models.
© 2021 The Authors. CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures

References
-
- Manceau H, Amrani K, Peoc’h K. Personalized medicine, pharmacogenomic and companion biomarker. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2017;75:631‐636. - PubMed
-
- Iriart JAB. Precision medicine/personalized medicine: a critical analysis of movements in the transformation of biomedicine in the early 21st century. Cad Saude Publica. 2019;35:e00153118. - PubMed
-
- Grissinger M. The five rights: a destination without a map. Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 2010;35:542.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

