What brain abnormalities can magnetic resonance imaging detect in foetal and early neonatal spina bifida: a systematic review
- PMID: 34792623
- PMCID: PMC8789702
- DOI: 10.1007/s00234-021-02853-1
What brain abnormalities can magnetic resonance imaging detect in foetal and early neonatal spina bifida: a systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: Open spina bifida (OSB) encompasses a wide spectrum of intracranial abnormalities. With foetal surgery as a new treatment option, robust intracranial imaging is important for comprehensive preoperative evaluation and prognostication. We aimed to determine the incidence of infratentorial and supratentorial findings detected by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) alone and MRI compared to ultrasound.
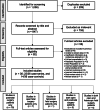
Methods: Two systematic reviews comparing MRI to ultrasound and MRI alone were conducted on MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases identifying studies of foetal OSB from 2000 to 2020. Intracranial imaging findings were analysed at ≤ 26 or > 26 weeks gestation and neonates (≤ 28 days). Data was independently extracted by two reviewers and meta-analysis was performed where possible.
Results: Thirty-six studies reported brain abnormalities detected by MRI alone in patients who previously had an ultrasound. Callosal dysgenesis was identified in 4/29 cases (2 foetuses ≤ 26 weeks, 1 foetus under any gestation, and 1 neonate ≤ 28 days) (15.1%, CI:5.7-34.3%). Heterotopia was identified in 7/40 foetuses ≤ 26 weeks (19.8%, CI:7.7-42.2%), 9/36 foetuses > 26 weeks (25.3%, CI:13.7-41.9%), and 64/250 neonates ≤ 28 days (26.9%, CI:15.3-42.8%). Additional abnormalities included aberrant cortical folding and other Chiari II malformation findings such as lower cervicomedullary kink level, tectal beaking, and hypoplastic tentorium. Eight studies compared MRI directly to ultrasound, but due to reporting inconsistencies, it was not possible to meta-analyse.
Conclusion: MRI is able to detect anomalies hitherto underestimated in foetal OSB which may be important for case selection. In view of increasing prenatal OSB surgery, further studies are required to assess developmental consequences of these findings.
Keywords: Foetal surgery; Intracranial anomaly; MRI; Spina bifida; Systematic review.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Scott Adzick N, Thom EA, Spong CY, Brock JW, Burrows PK, Johnson MP, Howell LJ, Farrell JA, Dabrowiak ME, Sutton LN, Gupta N, Tulipan NB, D’Alton ME, Farmer DL. A randomised trial of prenatal versus postnatal repair of myelomeningocele. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:993–1004. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1014379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araujo Junior E, Nakano ML, Nardozza LM, Haratz KK, Oliveira PS, Martins WP, Ajzen SA, Moron AF. Comparison between 2D ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging for assessing brain and spine parameters in fetuses with spina bifida. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2013;287(5):845–849. doi: 10.1007/s00404-012-2656-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

