Further exploration of the structure-activity relationship of dual soluble epoxide hydrolase/fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors
- PMID: 34794001
- PMCID: PMC8900675
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116507
Further exploration of the structure-activity relationship of dual soluble epoxide hydrolase/fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors
Abstract
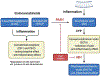
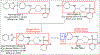
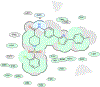
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is a membrane protein that hydrolyzes endocannabinoids, and its inhibition produces analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. The soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) hydrolyzes epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) to dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids. EETs have anti-inflammatory and inflammation resolving properties, thus inhibition of sEH consequently reduces inflammation. Concurrent inhibition of both enzymes may represent a novel approach in the treatment of chronic pain. Drugs with multiple targets can provide a superior therapeutic effect and a decrease in side effects compared to ligands with single targets. Previously, microwave-assisted methodologies were employed to synthesize libraries of benzothiazole analogs from which high affinity dual inhibitors (e.g. 3, sEH IC50 = 9.6 nM; FAAH IC50 = 7 nM) were identified. Here, our structure-activity relationship studies revealed that the 4-phenylthiazole moiety is well tolerated by both enzymes, producing excellent inhibition potencies in the low nanomolar range (e.g. 6o, sEH IC50 = 2.5 nM; FAAH IC50 = 9.8 nM). Docking experiments show that the new class of dual inhibitors bind within the catalytic sites of both enzymes. Prediction of several pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic properties suggest that these new dual inhibitors are good candidates for further in vivo evaluation. Finally, dual inhibitor 3 was tested in the Formalin Test, a rat model of acute inflammatory pain. The data indicate that 3 produces antinociception against the inflammatory phase of the Formalin Test in vivo and is metabolically stable following intraperitoneal administration in male rats. Further, antinociception produced by 3 is comparable to that of ketoprofen, a traditional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. The results presented here will help toward the long-term goal of developing novel non-opioid therapeutics for pain management.
Keywords: 4-Phenylthiazole moiety; ADMET predictions; Docking experiments; Enzyme inhibition; Formalin test; Microwave-assisted synthesis; Polypharmacology; Structure-Activity Relationship study.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
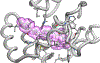

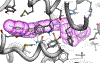
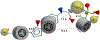

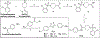
References
-
- Russo CM; Brose WG, Chronic pain. Annu Rev Med 1998, 49, 123–33. - PubMed
-
- Smith BH; Elliott AM; Chambers WA; Smith WC; Hannaford PC; Penny K, The impact of chronic pain in the community. Fam Pract 2001, 18 (3), 292–9. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y; Hong Y; Huang H, Triptolide Attenuates Inflammatory Response in Membranous Glomerulo-Nephritis Rat via Downregulation of NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Kidney Blood Press Res 2016, 41 (6), 901–910. - PubMed
-
- Marchand F; Perretti M; McMahon SB, Role of the immune system in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2005, 6 (7), 521–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

