A fully automatic system to assess foot collapse on lateral weight-bearing foot radiographs: A pilot study
- PMID: 34794087
- PMCID: PMC8674729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106507
A fully automatic system to assess foot collapse on lateral weight-bearing foot radiographs: A pilot study
Abstract
Background: Foot collapse is primarily diagnosed and monitored using lateral weight-bearing foot x-ray images. There are several well-validated measurements which aid assessment. However, these are subject to inter- and intra-user variability.
Objective: To develop and validate a software system for the fully automatic assessment of radiographic changes associated with foot collapse; automatically generating measurements for calcaneal tilt, cuboid height and Meary's angle.
Methods: This retrospective study was approved by the Health Research Authority (IRAS 244852). The system was developed using lateral weight-bearing foot x-ray images, and evaluated against manual measurements from five clinical experts. The system has two main components: (i) a Random Forest-based point-finder to outline the bones of interest; and (ii) a geometry-calculator to generate the measurements based on the point positions from the point-finder. The performance of the point-finder was assessed using the point-to-point error (i.e. the mean absolute distance between each found point and the equivalent ground truth point, averaged over all points per image). For assessing the performance of the geometry-calculator, linear mixed models were fitted to estimate clinical inter-observer agreement and to compare the performance of the software system to that of the clinical experts.
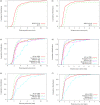
Results: A total of 200 images were collected from 79 subjects (mean age: 56.4 years ±12.9 SD, 30/49 females/males). There was good agreement among all clinical experts with intraclass correlation estimates between 0.78 and 0.86. The point-finder achieved a median point-to-point error of 2.2 mm. There was no significant difference between the clinical and automatically generated measurements using the point-finder points, suggesting that the fully automatically obtained measurements are in agreement with the manually obtained measurements.
Conclusions: The proposed system can be used to support and automate radiographic image assessment for diagnosing and managing foot collapse, saving clinician time, and improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: Charcot foot; Clinical decision support system; Diabetes; Landmark localization; Radiomics.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare not to have any conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Schon L.C., Weinfeld S.B., Horton G.A., Resch S. Radiographic and clinical classification of acquired midtarsus deformities. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19(6):394–404. - PubMed
-
- Sella E.J., Barrette C. Staging of Charcot neuroarthropathy along the medial column of the foot in the diabetic patient. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 1999;38(1):34–40. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt B.M., Holmes C.M. Updates on diabetic foot, charcot osteopathic arthropathy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018;18(10):74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

