Studying Motivation in ADHD: The Role of Internal Motives and the Relevance of Self Determination Theory
- PMID: 34794343
- PMCID: PMC9066661
- DOI: 10.1177/10870547211050948
Studying Motivation in ADHD: The Role of Internal Motives and the Relevance of Self Determination Theory
Abstract
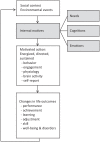
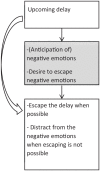
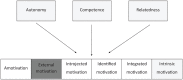
Objective: Motivation is what moves us to act, what engages us in goal-directed behavior. The Self Determination Theory (SDT) is a motivational framework conceptualizing motivation-or internal motives-as a continuum of motivation qualities fueled by satisfaction of the three basic psychological needs Autonomy, Relatedness, and Competence. ADHD has been associated with motivational alterations that contribute to academic difficulties. However, ADHD theories and research are mainly focused on the effects of reinforcement on behavior, with little attention for the broader definition of motivation, that is, internal motives. Therefore, the main objective here was to introduce the SDT as theoretical framework within which we can develop relevant research questions about motivation in the field of ADHD.
Method: To this end, we (i) present the SDT as a comprehensive motivational framework, and (ii) describe current motivation-related ADHD theories and research.
Results: Based on this, we suggest how SDT can be used as a guiding framework in generating relevant research questions that can help broaden our understanding of the role motivation plays in individuals with ADHD.
Conclusion: We conclude that ADHD research on motivation would benefit from (i) including internal motives as potential key mediators in the relation between environmental factors and behavior/symptoms; (ii) studying potential negative effects of external reinforcers intrinsic motivation, affect, and well-being. Finally, we conclude that this framework carries value for further development of clinical interventions for those with ADHD.
Keywords: ADHD; motivation; reinforcement; reward; self determination theory.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Aelterman N., Vansteenkiste M., Van Den Berghe L., De Meyer J., Haerens L. (2014). Fostering a need-supportive teaching style: Intervention effects on physical education teachers’ beliefs and teaching behaviors. Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology, 36(6), 595–609. - PubMed
-
- Aelterman N., Vansteenkiste M., Van Keer H., De Meyer J., Van Den Berghe L., Haerens L. (2013). Development and evaluation of a training on need-supportive teaching in physical education: Qualitative and quantitative findings. Teaching and Teacher Education, 29, 64–75.
-
- Aelterman N., Vansteenkiste M., Van Keer H., Haerens L. (2016). Changing teachers’ beliefs regarding autonomy support and structure: The role of experienced psychological need satisfaction in teacher training. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 23, 64–72.
-
- Ahmann E., Tuttle L. J., Saviet M., Wright S. D. (2018). A descriptive review of ADHD coaching research: Implications for college students. Journal of Postsecondary Education and Disability, 31, 17–39.
-
- Algozzine B., Browder D., Karvonen M., Test D. W., Wood W. M. (2001). Effects of interventions to promote self-determination for individuals with disabilities. Review of Educational Research, 71(2), 219–277.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

