Investigation of bioluminescence-based assays for determination of kinetic parameters for the bifunctional Neisseria meningitidis serogroup W capsule polymerase
- PMID: 34794506
- PMCID: PMC8600345
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-021-05831-1
Investigation of bioluminescence-based assays for determination of kinetic parameters for the bifunctional Neisseria meningitidis serogroup W capsule polymerase
Abstract
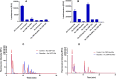
Objective: Neisseria meningitidis is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes meningitis. N. meningitidis serogroup W (NmW) capsule polymerase synthesizes capsular polysaccharide of this serogroup. This enzyme could be a tool for meningococcal glycoconjugate vaccine development. Our long-term goal is to control activity of the NmW capsule polymerase for production of defined carbohydrates for vaccines. The enzyme lacks a simple, high-throughput activity assay. Here, we describe the use of high-throughput bioluminescence assays (CMP-Glo and UDP-Glo by Promega) to investigate NmW capsule polymerase activity. These assays detect free nucleotides produced during transfer of sugar from UDP-Galactose and CMP-Sialic Acid to an acceptor. Kinetic studies using NmW hydrolyzed polysaccharide (PS) acceptor are described as well as preliminary work with a sialic acid trimer (DP3) acceptor.
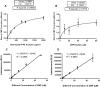
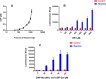
Results: In CMP-Glo kinetic studies, with constant donor (80 µM) and varied NmW hydrolyzed polysaccharide (0-2000 µg/mL), a Km of 629.2 ± 101.4 µg/mL and a Vmax of 0.8965 ± 0.05823 µM/min was obtained. Using UDP-Glo, Km and Vmax values of 13.84 ± 9.675 µM and 0.6205 ± 0.1331 µM/min were obtained with varied CMP-NeuNAc (0-80 µM) and constant acceptor (400 µg/mL) and UDP-Gal (80 µM). This is the first report of using bioluminescence assays for NmW kinetics.
Keywords: Bioluminescence assay; CMP-Glo; Kinetics; Neisseria meningitidis; UDP-Glo.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Borrow R, Alarcón P, Carlos J, Caugant DA, Christensen H, Debbag R, et al. The Global Meningococcal Initiative: global epidemiology, the impact of vaccines on meningococcal disease and the importance of herd protection. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2017;16(4):313–328. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2017.1258308. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Romanow A, Keys TG, Stummeyer K, Freiberger F, Henrissat B, Gerardy-Schahn R. Dissection of hexosyl- and sialyltransferase domains in the bifunctional capsule polymerases from Neisseriameningitidis W and Y defines a new sialyltransferase family. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(49):33945–33957. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.597773. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Romanow A, Haselhorst T, Stummeyer K, Claus H, Bethe A, Mühlenhoff M, et al. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of the sialyl-/hexosyltransferase synthesizing the meningococcal serogroup W135 heteropolysaccharide capsule. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(17):11718–11730. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.452276. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

