Immune cell topography predicts response to PD-1 blockade in cutaneous T cell lymphoma
- PMID: 34795254
- PMCID: PMC8602403
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-26974-6
Immune cell topography predicts response to PD-1 blockade in cutaneous T cell lymphoma
Abstract
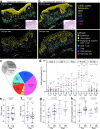
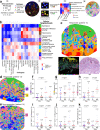
Cutaneous T cell lymphomas (CTCL) are rare but aggressive cancers without effective treatments. While a subset of patients derive benefit from PD-1 blockade, there is a critically unmet need for predictive biomarkers of response. Herein, we perform CODEX multiplexed tissue imaging and RNA sequencing on 70 tumor regions from 14 advanced CTCL patients enrolled in a pembrolizumab clinical trial (NCT02243579). We find no differences in the frequencies of immune or tumor cells between responders and non-responders. Instead, we identify topographical differences between effector PD-1+ CD4+ T cells, tumor cells, and immunosuppressive Tregs, from which we derive a spatial biomarker, termed the SpatialScore, that correlates strongly with pembrolizumab response in CTCL. The SpatialScore coincides with differences in the functional immune state of the tumor microenvironment, T cell function, and tumor cell-specific chemokine recruitment and is validated using a simplified, clinically accessible tissue imaging platform. Collectively, these results provide a paradigm for investigating the spatial balance of effector and suppressive T cell activity and broadly leveraging this biomarker approach to inform the clinical use of immunotherapies.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.P.N. and Y.G. are co-founders and stockholders of Akoya Biosciences, Inc. and inventors on patent US9909167 (On-slide staining by primer extension). D.P., C.M.S., and G.P.N. are inventors on pending patent US62971722 (Spatial method to predict immunotherapy outcome in cancer), filed by Stanford University. C.M.S. is a scientific advisor to Enable Medicine, LLC. Y.H.K. received research funding from Merck & Co. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Wilcox RA. Mogamulizumab: 2 birds, 1 stone. Blood. 2015;125:1847–1848. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UG3 DK114937/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI100627/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI101984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG010426/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F99 CA212231/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI140498/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA233203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135976/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA154967/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI131374/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 27145/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- T32 AI007290/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057229/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U2C CA233238/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C27165/A29073/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA154967/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U2C CA233195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 CA183692/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007422/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

