Effects of call reminders, short message services (SMS) reminders, and SMS immunization facts on childhood routine vaccination timing and completion in Ilorin, Nigeria
- PMID: 34795755
- PMCID: PMC8568234
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v21i2.57
Effects of call reminders, short message services (SMS) reminders, and SMS immunization facts on childhood routine vaccination timing and completion in Ilorin, Nigeria
Abstract
Background: Reminders via mobile devices deployed as short message services (SMS) or calls have been identified to be a useful strategy in improving routine immunization uptake in several countries.
Objective: To identify the timeliness of appointments with reminders (calls or SMS), SMS health education and the routine care, and the vaccination completion rates in Ilorin, Nigeria.
Method: Mother-infant pairs presenting for the first vaccination appointment were randomized into four (three interventions, one control) groups, each consisting of 140 participants. Intervention groups were reminders via calls (A), SMS reminders (B), immunization fact SMS messages (C) and controls on usual care (D). Reminders were made a day before the appointment while SMS immunization facts were sent at five weeks, nine weeks and eight months. Appropriate timing was defined as the scheduled visit ±3 days.
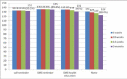
Results: The immunization completion rates after the nine months' visit were 99.2%, 99.3%, 97% and 90.4% for Groups A, B, C and D respectively. Compared with controls, Group A had the highest odds [AOR 8.78 (6.10, 12.63)] of presenting at an appropriate time, followed by Group B [AOR 2.56 (1.96, 3.35)], then Group C [AOR 2.44 (1.87, 3.18)].
Conclusion: Reminders/SMS immunization facts improve vaccination completion rates.
Keywords: Call reminders; Nigeria; SMS immunization; short message services (SMS) reminders; vaccination timing.
© 2021 Ibaheem R et al.
Figures
References
-
- WHO, author. Immunization coverage fact sheet. 2018.
-
- National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) and United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), author Multiple indicator cluster survey 2016–17 Survey Findings Report. Abuja, Nigeria: National Bureau of Statistics and United Nations Children's Fund. 2017.
-
- Onyiriuka A. Vaccination default rates among children attending a static immunization clinic in Benin city, Nigeria. J Med Biomed Res. 2005;4:71–77. PubMed.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous