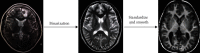
Diagnosis of Schizophrenia Based on Deep Learning Using fMRI
- PMID: 34795793
- PMCID: PMC8594998
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8437260
Diagnosis of Schizophrenia Based on Deep Learning Using fMRI
Abstract
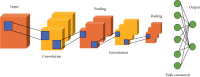
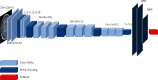
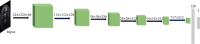
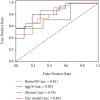
Schizophrenia is a brain disease that frequently occurs in young people. Early diagnosis and treatment can reduce family burdens and reduce social costs. There is no objective evaluation index for schizophrenia. In order to improve the classification effect of traditional classification methods on magnetic resonance data, a method of classification of functional magnetic resonance imaging data is proposed in conjunction with the convolutional neural network algorithm. We take functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data for schizophrenia as an example, to extract effective time series from preprocessed fMRI data, and perform correlation analysis on regions of interest, using transfer learning and VGG16 net, and the functional connection between schizophrenia and healthy controls is classified. Experimental results show that the classification accuracy of fMRI based on VGG16 is up to 84.3%. On the one hand, it can improve the early diagnosis of schizophrenia, and on the other hand, it can solve the classification problem of small samples and high-dimensional data and effectively improve the generalization ability of deep learning models.
Copyright © 2021 JinChi Zheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease Severity with fMRI Images Using Robust Multitask Feature Extraction Method and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN).Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Apr 27;2021:5514839. doi: 10.1155/2021/5514839. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34007305 Free PMC article.
-
3D-CNN based discrimination of schizophrenia using resting-state fMRI.Artif Intell Med. 2019 Jul;98:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Jun 22. Artif Intell Med. 2019. PMID: 31521248
-
Brain Decoding Using fMRI Images for Multiple Subjects through Deep Learning.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Mar 1;2022:1124927. doi: 10.1155/2022/1124927. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Aug 2;2023:9785636. doi: 10.1155/2023/9785636. PMID: 35273647 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Application of deep canonically correlated sparse autoencoder for the classification of schizophrenia.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Jan;183:105073. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105073. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 31525548
-
Unveiling the potential of machine learning in schizophrenia diagnosis: A meta-analytic study of task-based neuroimaging data.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Mar;78(3):157-168. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13625. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38013639 Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding Schizophrenia: How AI-Enhanced fMRI Unlocks New Pathways for Precision Psychiatry.Brain Sci. 2024 Nov 27;14(12):1196. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14121196. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39766395 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring deep residual network based features for automatic schizophrenia detection from EEG.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2023 Jun;46(2):561-574. doi: 10.1007/s13246-023-01225-8. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2023. PMID: 36947384 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-cohort replicable resting-state functional connectivity in predicting symptoms and cognition of schizophrenia.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 May;45(7):e26694. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26694. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 38727014 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Association Between Heavy Metals, TNF-α Regulation, and Cognitive Dysfunction in Schizophrenia.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Jun 18. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04701-2. Online ahead of print. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 40533715
-
Towards greater neuroimaging classification transparency via the integration of explainability methods and confidence estimation approaches.Inform Med Unlocked. 2023;37:101176. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2023.101176. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Inform Med Unlocked. 2023. PMID: 37035832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Key S. The positive and negative syndrome (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry . 1987;20
-
- Tang Z., Zhao G., Ouyang T. Two-phase deep learning model for short-term wind direction forecasting. Renewable Energy . 2021;173(72):1005–1016. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.04.041. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical