Artificial Intelligence in Neurosurgery: a Systematic Review Using Topic Modeling. Part I: Major Research Areas
- PMID: 34796011
- PMCID: PMC8596264
- DOI: 10.17691/stm2020.12.5.12
Artificial Intelligence in Neurosurgery: a Systematic Review Using Topic Modeling. Part I: Major Research Areas
Abstract
In recent years, the number of scientific publications on artificial intelligence (AI), primarily on machine learning, with respect to neurosurgery, has increased. The aim of the study was to conduct a systematic literature review and identify the main areas of AI applications in neurosurgery.
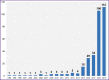
Methods: Using the PubMed search engine, we found and analyzed 327 original articles published in 1996-2019. The key words specific to each topic were identified using topic modeling algorithms LDA and ARTM, which are part of the AI-based natural language processing.
Results: Five main areas of neurosurgery, in which research into AI methods are underway, have been identified: neuro-oncology, functional neurosurgery, vascular neurosurgery, spinal neurosurgery, and surgery of traumatic brain injury. Specifics of these studies are characterized.
Conclusion: The information presented in this review can be instrumental in planning new research projects in neurosurgery.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; machine learning; natural language processing; neurosurgery; topic modeling in neurosurgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest. The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ng A. What artificial intelligence can and can’t do right now. Harv Bus Rev. 2016.
-
- Yakushev D.I. Ob opredelenii iskusstvennogo intellekta. V kn.: Regional’naya informatika i informatsionnaya bezopasnost’ [On the definition of artificial intelligence. In: Regional informatics and information security proceedings]. Saint Peterburg: 2016. pp. 67–69.
-
- Luger J.F. Iskusstvennyy intellekt: strategii i metody resheniya slozhnykh problem. Moscow: Izdatel’skiy dom “Vil’yams”; 2003. [Artificial intelligence: strategies and methods for solving complex problems].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources