The red flags of ulnar neuropathy in leprosy
- PMID: 34797866
- PMCID: PMC8604365
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259804
The red flags of ulnar neuropathy in leprosy
Abstract
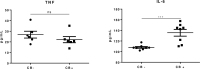
The diagnosis of pure neural leprosy is more challenging because patients share characteristics with other common pathologies, such as ulnar compression, which should be taken into consideration for differential diagnosis. In this study, we identify ulnar nerve conduction characteristics to aid in the differential diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy (UN) in leprosy and that of non-leprosy etiology. In addition, we include putative markers to better understand the inflammatory process that may occur in the nerve. Data were extracted from a database of people affected by leprosy (leprosy group) diagnosed with UN at leprosy diagnosis. A non-leprosy group of patients diagnosed with mechanical neuropathy (compressive, traumatic) was also included. Both groups were submitted to clinical, neurological, neurophysiological and immunological studies. Nerve enlargement and sensory impairment were significantly higher in leprosy patients than in patients with compressive UN. Bilateral impairment was significantly higher in the leprosy group than in the non-leprosy group. Leprosy reactions were associated to focal demyelinating lesions at the elbow and to temporal dispersion (TD). Clinical signs such as sensory impairment, nerve enlargement and bilateral ulnar nerve injury associated with eletrodiagnostic criteria such as demyelinating finds, specifically temporal dispersion, could be tools to help us decided on the best conduct in patients with elbow ulnar neuropathy and specifically decide if we should perform a nerve biopsy for diagnosis of pure neural leprosy.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have competing interests.
Figures
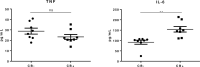
References
-
- Dumitru D ZM. Focal peripheral neuropathies. In: Dumitru D AA, Zwarts MJ, ed. Electrodiagnostic Medicine. 2 ed. Philadelphia: Hanley and Belfus; 2002:1043–126.
-
- Kitzinger HB AO, Moser VL, Frey M. Significance of electroneurographic parameters in the diagnosis of chronic neuropathy of the ulnar nerve at the elbow. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2005;4(37):276–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

