Effect of exposure to etidronic acid on the bond strength of calcium silicate-based cements after 1 and 21 days: an in vitro study
- PMID: 34798880
- PMCID: PMC8603527
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-021-01959-5
Effect of exposure to etidronic acid on the bond strength of calcium silicate-based cements after 1 and 21 days: an in vitro study
Abstract
Background: After reparation of root perforations with calcium silicate-based cements (CSBC), the surface of the material is expected to be exposed to root canal irrigants (RCI) while resuming the root canal treatment.
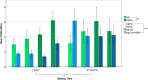
Methods: The aim of this study was to compare the effect of exposure to a mixture of sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and etidronic acid (HEBP) or other irrigants on the Push Out Bond Strength (POBS) of CSBC after two different setting times. 240 root slices 1 mm thick were obtained from single-rooted human teeth. A 1.4 mm diameter perforation was performed on each slice and filled with Biodentine (BD) or ProRoot MTA (PMTA). After 1 or 21 days they were exposed to 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 5.25% NaOCl, a mixture of 5.25% NaOCl and 9% HEBP (NaOCl + HEBP) or saline (n = 15) and submitted to a push-out test. POBS results were analysed with ANOVA and Tukey tests.
Results: BD showed higher POBS than PMTA after 1 day (p < .05). After 21 days no differences were found between materials. After 1 day exposure to NaOCl + HEBP resulted in higher POBS, compared to the other irrigants (p < .05).
Conclusion: POBS results are influenced by the cement, the setting time and the exposure to irrigants.
Keywords: Bond strength; Calcium silicate cements; Etidronic acid; Root canal irrigants; Setting time.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

