Immune reactivity and host modulatory roles of two novel Haemonchus contortus cathepsin B-like proteases
- PMID: 34798906
- PMCID: PMC8603344
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-021-05010-y
Immune reactivity and host modulatory roles of two novel Haemonchus contortus cathepsin B-like proteases
Abstract
Background: Haemonchus contortus is a blood-feeding, gastrointestinal nematode (GIN) that causes significant economic losses to the small ruminant industry worldwide. Despite extensive efforts, our understanding of the molecular mechanisms used by GIN to evade host immune responses is limited. Cathepsin B-like proteins (CBPs) are members of the cysteine protease family and are involved in parasite invasion and thus provide viable vaccine candidates.
Methods: In silico comparative analysis was used to identify conserved proteins among a subset of clade V parasitic nematodes with emphasis on blood-feeding worms, among which CBPs appeared prominently. We identified and characterized two novel CBPs designated Hc-CBP-1 and Hc-CBP-2. Rabbit anti-recombinant (r) Hc-CBP-1 and rHc-CBP-2 were used to detect the presence of native proteins in the excretory secretory products (ESP) and in worm tissues of adult H. contortus. Peptide arrays of rHc-CBP-1 and rHc-CBP-2 were screened with the homologous and heterologous anti-sera and with sera from dexamethasone-treated (Dex+) and non-treated (Dex-) H. contortus-infected animals to identify key immunogenic peptides. Gene transcription of Hc-cbp-1 and Hc-cbp-2 was also performed on H. contortus-infected animals treated with Dex+. Finally, the mature recombinant proteins were used to assess their abilities to modulate cell functions.
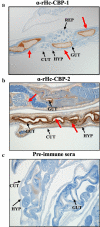
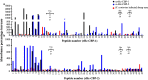
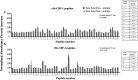
Results: Immunohistochemistry showed that both Hc-CBP-1 and Hc-CBP-2 are present on the brush borders of the intestine; Hc-CBP-2 was also present in the hypodermis of the body wall. Peptide displays screened with rabbit anti-rHc-CBP-1 and anti-rHc-CBP-2 revealed regions within the proteins where dominant and overlapping epitopes prevailed. ELISA results were consistent with only Hc-CBP-1 being present in H. contortus adult ESPs. H. contortus from Dex+ animals exhibited a threefold increase in Hc-cbp-2 transcript while Hc-cbp-1 expression did not change. In contrast, comparisons of immunoreactivities of rHc-CBP-1 and rHc-CBP-2 peptide arrays to sera from Dex+ and Dex- animals primarily showed changes in Hc-CBP-1 binding. Lastly, rHc-CBP-1 suppressed mRNA expression of bovine peripheral blood mononuclear cell cytokines/activation markers, including TNFα, IL-1, IL-6 and CD86.
Conclusions: These results suggest that as secreted and cryptic proteins, respectively, Hc-CBP-1 and Hc-CBP-2 influence cellular and immunological activities that have interesting dynamics during infection and may provide viable immune-related targets for attenuating H. contortus infectivity.
Keywords: Cathepsin B; Cysteine proteases; Gastrointestinal; Haemonchus contortus; Peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Arginine kinase from Haemonchus contortus decreased the proliferation and increased the apoptosis of goat PBMCs in vitro.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Jun 26;10(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2244-z. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28651566 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin Domain Containing Protein from Haemonchus contortus Modulates the Immune Functions of Goat PBMCs and Regulates CD4+ T-Helper Cells In Vitro.Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 9;10(1):116. doi: 10.3390/biom10010116. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31936604 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a secreted cystatin of the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus and its immune-modulatory effect on goat monocytes.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Sep 18;10(1):425. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2368-1. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28923082 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Haemonchus contortus Excretory and Secretory Proteins (HcESPs): TH-9 stimulated ESPs as a potential candidate for Vaccine Development and Diagnostic Antigen.Acta Trop. 2024 Dec;260:107462. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2024.107462. Epub 2024 Nov 10. Acta Trop. 2024. PMID: 39527996 Review.
-
The complement of family M1 aminopeptidases of Haemonchus contortus--Biotechnological implications.Biotechnol Adv. 2016 Mar-Apr;34(2):65-76. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.10.003. Epub 2015 Oct 24. Biotechnol Adv. 2016. PMID: 26597954 Review.
Cited by
-
PLGA-Encapsulated Haemonchus contortus Antigen ES-15 Augments Immune Responses in a Murine Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;11(12):1794. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11121794. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38140198 Free PMC article.
-
Echinococcus multilocularis serpin regulates macrophage polarization and reduces gut dysbiosis in colitis.Infect Immun. 2024 Aug 13;92(8):e0023224. doi: 10.1128/iai.00232-24. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 39037247 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of Haemonchus contortus Proteases and Protease Inhibitors Using Advanced Informatics Provides Insights into Parasite Biology and Host-Parasite Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 1;24(15):12320. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512320. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569696 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Profiling of Abomasal Mucosa from Young Calves Experimentally Infected with Ostertagia ostertagi.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 4;26(5):2264. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052264. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076885 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and immunoprotective functions of three cysteine proteases from Clonorchis sinensis.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 3;16:1550775. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1550775. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40248698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perry BD. Investing in animal health research to alleviate poverty: ILRI (aka ILCA and ILRAD); 2002.
-
- Prichard R. Genetic variability following selection of Haemonchus contortus with anthelmintics. Trends Parasitol. 2001;17(9):445–453. - PubMed
-
- Clark CH, Kiesel GK, Goby CH. Measurement of blood loss caused by Haemonchus contortus. Am J Vet Med. 1962;23:977–980. - PubMed
-
- Kotze A, Prichard R. Anthelmintic resistance in Haemonchus contortus: history, mechanisms and diagnosis. Adv Parasitol. 2016;93:397–428. - PubMed
-
- Lightowlers M, Rickard M. Excretory–secretory products of helminth parasites: effects on host immune responses. Parasitology. 1988;96(S1):S123–S166. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

