Nonlinear relationship between HbA1c and coronary artery calcium score progression: a secondary analysis based on a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 34798910
- PMCID: PMC8603599
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-021-00747-z
Nonlinear relationship between HbA1c and coronary artery calcium score progression: a secondary analysis based on a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: Coronary artery calcium score and glycated hemoglobin(HbA1c) are both considered risk factors for coronary heart disease. However, the relationship between coronary artery calcium score and HbA1c is still unclear. Consequently, the present study was undertaken to explore HbA1c association with coronary artery calcium score progression in South Korea.
Methods: This study is a secondary analysis based on a retrospective cohort study in which 8151 participants received Health examination kits at the Health Promotion Center, Samsung Medical Center in Seoul, South Korea, from March 1, 2003-December 31, 2013. Cox proportional-hazards regression model was then used to evaluate the independent relationship between HbA1c and coronary artery calcium score progression.
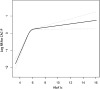
Results: After adjusting potential confounding factors (age, sex, BMI, height, weight, SBP, DBP, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides, smoking status, alcohol consumption, reflux esophagitis status, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, ischemic heart disease and cerebrovascular disease), it was revealed that there was a nonlinear relationship between HbA1c and coronary artery calcium score progression, while the scoring point was 5.8%. The effect size was 2.06 to the left of the inflection point, while the 95% CI was 1.85 to 2.29. Whereas, the effect size was 1.04, on the right side of the inflection point while 95% CI was 0.99 to1.10.
Conclusion: The relationship between HbA1c and coronary artery calcium score progression is nonlinear. HbA1c is positively related to coronary artery calcium score progression when HbA1c level was less than 5.8%.
Keywords: Coronary artery calcium score; Coronary atherosclerotic heart disease; Glycated hemoglobin.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources