Pharmacokinetics of bempedoic acid in patients with renal impairment
- PMID: 34800002
- PMCID: PMC8932715
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.13202
Pharmacokinetics of bempedoic acid in patients with renal impairment
Abstract
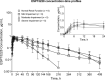
Bempedoic acid is an ATP citrate lyase inhibitor approved for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. The objective of this phase I study was to assess the pharmacokinetics (PKs) and safety of bempedoic acid in 24 subjects with normal renal function or mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment. All subjects received a single oral bempedoic acid 180-mg dose and PK parameters were monitored for up to 23 days. Resulting estimates of area under the concentration-time curve exposure following bempedoic acid treatment were 1.5-fold, 2.2-fold, and 2.2-fold higher in subjects with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment, respectively, compared with subjects with normal renal function. With decreases in renal function, plasma free fraction was increased up to 20.1%, whereas total and unbound clearances were decreased by 55.2% and 62.6%, respectively, in subjects with severe renal impairment relative to those with normal renal function. These observed decreases in total and unbound oral clearance in subjects with decreased renal function are not explained by the increases in free fraction and might therefore also be attributable to changes in bioavailability or intrinsic clearance. Bempedoic acid was generally well-tolerated and the incidence and type of adverse events were not affected by the degree of renal impairment. In conclusion, bempedoic acid exposures in subjects with renal impairment were increased up to approximately two-fold with no safety signals identified, consistent with findings in phase III patients with mild or moderate renal impairment. No dose adjustments are necessary for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment.
© 2021 Esperion Therapeutics, Inc. Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
B.M.A., M.G.E., W.J.S., and P.T. are current (B.M.A.) or former (M.G.E., W.J.S., and P.T.) employees of Esperion Therapeutics, Inc., and may hold stock and/or stock options. W.J.S. is currently the Principal of Cardiometabolic Consulting, LLC. D.K.R. is a current employee of Nucleus Network, Pty, Ltd., which had a corporate agreement with Esperion Therapeutics, Inc., during this study.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Chronic kidney disease in the United States (2021). https://www.cdc.gov/kidneydisease/publications‐resources/ckd‐national‐fa.... Accessed April 6, 2021.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Chronic kidney disease risk factors and prevention (2021). https://www.cdc.gov/kidneydisease/publications‐resources/annual‐report/c.... Accessed April 6, 2021.
-
- US Food and Drug Administration, Draft Guidance: Pharmacokinetics in patients with impaired renal function — study design, data analysis, and impact on dosing and labeling (2020). https://www.fda.gov/media/78573/download. Accessed April 6, 2021.
-
- European Medicines Agency, Guideline on the evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of medicinal products in patients with decreased renal function (2016). https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific‐guideline/guideline‐ev.... Accessed April 6, 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

